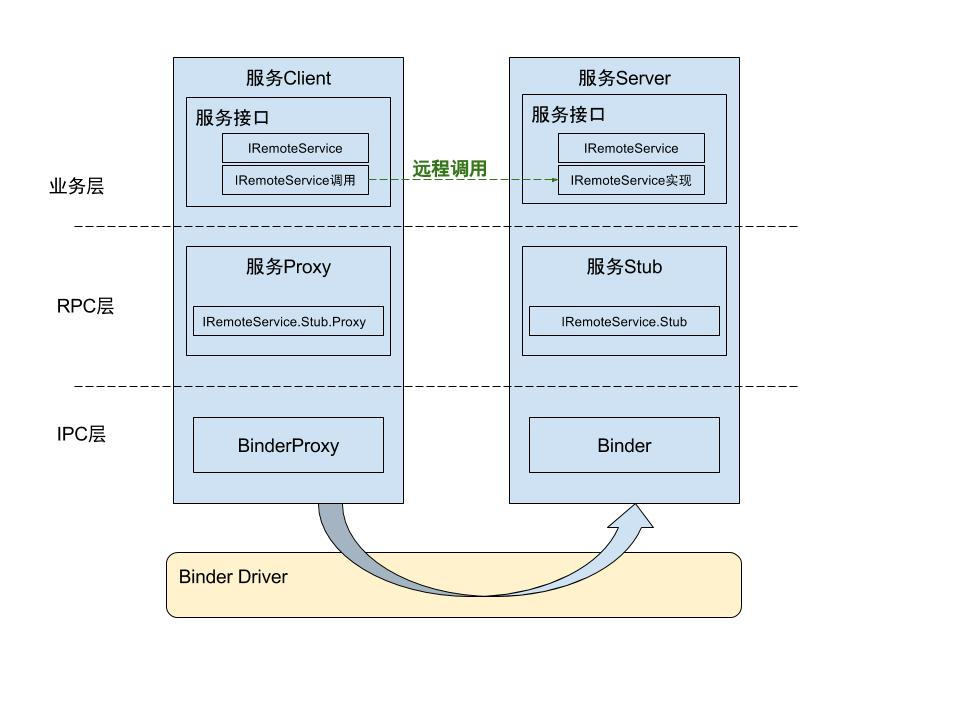
Binder作为Android系统中重要的进程间通信方式,了解其基本的原理,对于分析问题具有重要的作用。由于Binder架构涉及的内容比较多,后面将会从应用层、框架层、Native层、内核层四个层次来说明Binder的原理。首先将从应用层的AIDL开始逐渐深入到内核层。
一、AIDL
在进行进程间通信时,需要将接口定义好,定义好之后创建aidl文件,将接口方法放在文件中。客户端和服务端,aidl文件要保持一致,包括包名。在build之后,会在客户端和服务端生成接口类。
1.aidl文件
[->IRemoteService.aidl]
// IRemoteService.aidl
package com.zhh.server;
interface IRemoteService {
void addPhone(String name);
boolean getPhone(String name);
int getPid();
}2.服务端
[->PhoneService.java]
package com.zhh.server;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PhoneService extends Service {
List<String> phones = new ArrayList<>();
//实现binder接口
private IRemoteService.Stub mBinder = new IRemoteService.Stub() {
@Override
public void addPhone(String name) throws RemoteException {
Log.d("phone binder","server add phone:"+name);
phones.add(name);
}
@Override
public boolean getPhone(String name) throws RemoteException {
Log.d("phone binder","server get phone:"+name);
if(phones.contains(name)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int getPid() throws RemoteException {
Log.d("phone binder","server getPid "+android.os.Process.myPid());
return android.os.Process.myPid();
}
@Override
public void linkToDeath(IBinder.DeathRecipient recipient, int flags) {
super.linkToDeath(recipient, flags);
Log.d("phone binder","server getPid linkToDeath");
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.d("phone binder","server onCreate");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.d("phone binder","server onBind");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.d("phone binder","server onUnbind");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.d("phone binder","server onDestroy");
super.onDestroy();
}
}3.客户端
[->MainActivity.java]
package com.zhh.client;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.design.widget.BottomNavigationView;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.zhh.server.IRemoteService;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView mTextMessage;
private IRemoteService mService;
private BottomNavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener mOnNavigationItemSelectedListener
= new BottomNavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem item) {
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.navigation_home:
mTextMessage.setText(R.string.title_home);
bindService();
return true;
case R.id.navigation_dashboard:
mTextMessage.setText(R.string.title_dashboard);
unbindService();
return true;
case R.id.navigation_notifications:
mTextMessage.setText(R.string.title_notifications);
killService();
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
BottomNavigationView navView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view);
mTextMessage = findViewById(R.id.message);
navView.setOnNavigationItemSelectedListener(mOnNavigationItemSelectedListener);
Log.d("phone binder","onCreate");
}
void bindService(){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.zhh.server","com.zhh.server.PhoneService"));
bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
void unbindService(){
if(mService!=null){
unbindService(connection);
}
}
void killService(){
try {
if(mService!=null){
android.os.Process.killProcess(mService.getPid());
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.d("phone binder","onServiceConnected");
try {
//获取代理
mService = IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface(service);
Log.d("phone binder","client getphone:"+mService.getPhone("apple"));
mService.addPhone("apple");
Log.d("phone binder","client getphone:"+mService.getPhone("apple"));
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.d("binder","onServiceDisconnected");
mService = null;
}
};
}
4.运行结果

点击客户端相应的控件,完成绑定服务,解绑服务,杀死service进程,日志如下:
16:09:10.394 27006-27006/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server onCreate
16:09:10.395 27006-27006/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server onBind
16:09:10.405 27006-27018/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server get phone:apple
16:09:10.407 27006-27018/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server add phone:apple
16:09:10.409 27006-27018/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server get phone:apple
16:16:55.497 27006-27006/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server onUnbind
16:16:55.502 27006-27006/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server onDestroy
16:16:57.955 27006-27020/com.zhh.server D/phone binder: server getPid 27006
二、AIDL原理分析
1. IRemoteService类
aidl生成一个对应的IRemoteService.java,其原理还是利用了framework binder的架构,具体的内部原理后面介绍,先分析下这个生成类,其流程如下:
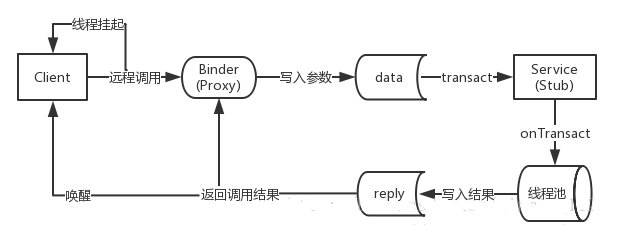
AIDL接口:继承IInterface。
Stub类:Binder的实现类,服务端通过这个类来提供服务。
Proxy类:服务器的本地代理,客户端通过这个类调用服务器的方法。
asInterface():客户端调用,将服务端的返回的Binder对象,转换成客户端所需要的AIDL接口类型对象。返回对象:
1.若客户端和服务端位于同一进程,则直接返回Stub对象本身;
2.否则,返回的是系统封装后的Stub.proxy对象。
asBinder():根据当前调用情况返回代理Proxy的Binder对象。
onTransact():运行服务端的Binder线程池中,当客户端发起跨进程请求时,远程请求会通过系统底层封装后交由此方法来处理。
transact():运行在客户端,当客户端发起远程请求的同时将当前线程挂起。之后调用服务端的onTransact()直到远程请求返回,当前线程才继续执行。
/*
* This file is auto-generated. DO NOT MODIFY.
* Original file: G:\\Android studio\\Aidl\\client\\src\\main\\aidl\\com\\zhh\\server\\IRemoteService.aidl
*/
package com.zhh.server;
public interface IRemoteService extends android.os.IInterface {
/**
* Local-side IPC implementation stub class.
*/
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.zhh.server.IRemoteService {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.zhh.server.IRemoteService";
/**
* Construct the stub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.zhh.server.IRemoteService interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.zhh.server.IRemoteService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.zhh.server.IRemoteService))) {
return ((com.zhh.server.IRemoteService) iin);
}
return new com.zhh.server.IRemoteService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(descriptor);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_addPhone: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
java.lang.String _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readString();
this.addPhone(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getPhone: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
java.lang.String _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readString();
boolean _result = this.getPhone(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(((_result) ? (1) : (0)));
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getPid: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
int _result = this.getPid();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
default: {
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
private static class Proxy implements com.zhh.server.IRemoteService {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public void addPhone(java.lang.String name) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeString(name);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_addPhone, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public boolean getPhone(java.lang.String name) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
boolean _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeString(name);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getPhone, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = (0 != _reply.readInt());
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
@Override
public int getPid() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getPid, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_addPhone = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
static final int TRANSACTION_getPhone = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
static final int TRANSACTION_getPid = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 2);
}
public void addPhone(java.lang.String name) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public boolean getPhone(java.lang.String name) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public int getPid() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}2. 原理
对于应用层来说bindService之后就可以和服务端进行交互了,可以不用里面具体的操作如何,这样的设计大大降低了使用了难度,对于binderService的具体的过程将在后面分析,下面是其分层次的调用图。