一、概述
每个app在启动前都必须创建一个进程,这个进程是由zygote fork而来,进程具有独立的资源空间,用于app上运行的各种Activity、Service等组件。大多数情况下一个应用运行在一个进程中,除非在AndroidManifest.xml中配置Android:process属性,或者通过Native代码fork进程。相对于线程,线程没有独立的地址空间,与其所在进程之间资源共享。
Android系统根据进程的重要性主要分为前台进程、可见进程、服务进程、后台进程、空进程。为了回收系统资源,系统会根据重要性高低来清除进程。
下图是进程的创建过程
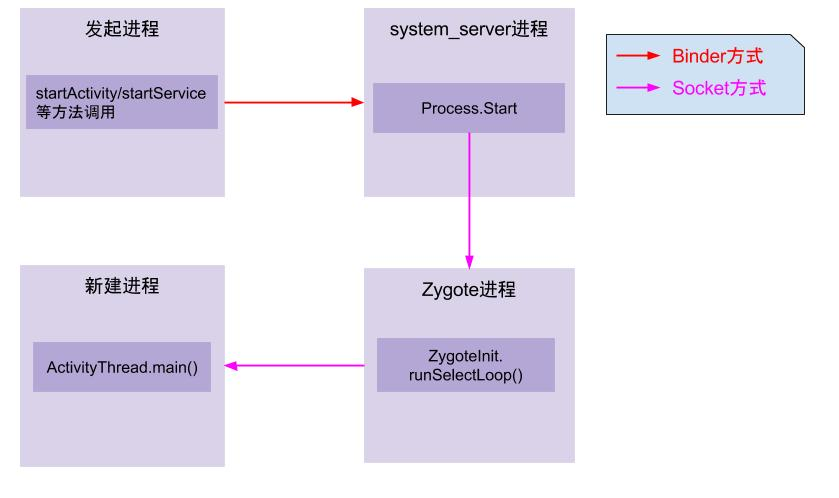
1.APP发起进程:当从桌面启动应用,则发起进程是Launcher所在进程;当从某App内启动远程进程,则发送进程是该app所在的进程。发送进程通过binder发送消息给systemserver进程。
2.systemserver进程:调用Process.start方法,通过socket向zygote进程发送创建新进程的请求。
3.zygote进程:执行ZygoteInit.main进入runSelectLoop循环体内,当有客户端连接时,便会执行ZygoteConnection.processOneCommand方法,经过层层调用fork新的应用进程。
4.新进程:执行handleChildProc方法,最后调用ActivityThread.main方法。
下面将从进程的角度分析进程创建的过程。
二、systemserver发起请求
1. Process.start
[->Process.java]
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
return ZYGOTE_PROCESS.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith,
/*useBlastulaPool=*/ true, zygoteArgs);
}
public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
boolean useBlastulaPool,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith,
/*startChildZygote=*/false,
useBlastulaPool, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}
2. Process.startViaZygote
[->ZygoteProcess.java]
private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
boolean startChildZygote,
boolean useBlastulaPool,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();
// --runtime-args, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-flags=" + runtimeFlags);
if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-default");
} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_READ) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-read");
} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_WRITE) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-write");
}
argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
// --setgroups is a comma-separated list
if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("--setgroups=");
int sz = gids.length;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(gids[i]);
}
argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
}
if (niceName != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
}
if (seInfo != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);
}
if (instructionSet != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--instruction-set=" + instructionSet);
}
if (appDataDir != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir);
}
if (invokeWith != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--invoke-with");
argsForZygote.add(invokeWith);
}
if (startChildZygote) {
argsForZygote.add("--start-child-zygote");
}
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
synchronized(mLock) {
//见第3节
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi),
useBlastulaPool,
argsForZygote);
}
}该过程主要是配置argsForZygote列表信息,列表信息保存了uid,gid,targetSdkVersion,appDataDir等信息。
3. zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult
[->ZygoteProcess.java]
private static Process.ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, boolean useBlastulaPool, ArrayList<String> args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
// Throw early if any of the arguments are malformed. This means we can
// avoid writing a partial response to the zygote.
for (String arg : args) {
if (arg.indexOf('/n') >= 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("embedded newlines not allowed");
}
}
/*
* See com.android.internal.os.ZygoteArguments.parseArgs()
* Presently the wire format to the zygote process is:
* a) a count of arguments (argc, in essence)
* b) a number of newline-separated argument strings equal to count
*
* After the zygote process reads these it will write the pid of
* the child or -1 on failure, followed by boolean to
* indicate whether a wrapper process was used.
*/
String msgStr = Integer.toString(args.size()) + "/n"
+ String.join("/n", args) + "/n";
// Should there be a timeout on this?
//这里等待创建进程返回是否加timeout?
Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
// TODO (chriswailes): Move branch body into separate function.
if (useBlastulaPool && Zygote.BLASTULA_POOL_ENABLED && isValidBlastulaCommand(args)) {
LocalSocket blastulaSessionSocket = null;
//blastulaSessionSocket进入这个分支
try {
blastulaSessionSocket = zygoteState.getBlastulaSessionSocket();
final BufferedWriter blastulaWriter =
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(blastulaSessionSocket.getOutputStream()),
Zygote.SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE);
final DataInputStream blastulaReader =
new DataInputStream(blastulaSessionSocket.getInputStream());
blastulaWriter.write(msgStr);
blastulaWriter.flush();
//等待socket服务端返回新创建的进程pid
result.pid = blastulaReader.readInt();
// Blastulas can't be used to spawn processes that need wrappers.
result.usingWrapper = false;
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Blastula specialization failed");
}
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
// If there was an IOException using the blastula pool we will log the error and
// attempt to start the process through the Zygote.
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "IO Exception while communicating with blastula pool - "
+ ex.toString());
} finally {
try {
blastulaSessionSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Failed to close blastula session socket: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
try {
final BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = zygoteState.mZygoteOutputWriter;
final DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = zygoteState.mZygoteInputStream;
zygoteWriter.write(msgStr);
zygoteWriter.flush();
// Always read the entire result from the input stream to avoid leaving
// bytes in the stream for future process starts to accidentally stumble
// upon.
//等待socket服务端返回新创建的进程pid
result.pid = zygoteInputStream.readInt();
result.usingWrapper = zygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "IO Exception while communicating with Zygote - "
+ ex.toString());
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
return result;
}这个方法主要是通过socket通道向zygote进程发送一个参数列表信息,然后进入阻塞等待状态,直到远端的socket服务端发送回来新创建的进程pid才返回。
3.1 openZygoteSocketIfNeeded
[->ZygoteProcess.java]
private ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.holdsLock(mLock), "ZygoteProcess lock not held");
if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
//向主zygote发起connect操作
primaryZygoteState =
ZygoteState.connect(mZygoteSocketAddress, mBlastulaPoolSocketAddress);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote", ioe);
}
maybeSetApiBlacklistExemptions(primaryZygoteState, false);
maybeSetHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate(primaryZygoteState);
}
if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return primaryZygoteState;
}
// The primary zygote didn't match. Try the secondary.
if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
//当主zygote不匹配,则采用第二个zygote发起connect连接
secondaryZygoteState =
ZygoteState.connect(mZygoteSecondarySocketAddress,
mBlastulaPoolSecondarySocketAddress);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote", ioe);
}
maybeSetApiBlacklistExemptions(secondaryZygoteState, false);
maybeSetHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate(secondaryZygoteState);
}
if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return secondaryZygoteState;
}
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
}
这个方法主要是根据abi来选择与zygote还是zygote64来进行通信。
在systemserver进程的zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法通过socket向zygote发送消息,这时会唤醒Zygote进程,来响应systemserver客户端的请求,下面是zygote来创建进程。
三、zygote创建进程
在systemserver启动过程上中有介绍zygote进程启动,它是由init进程创建,进程启动之后调用ZygoteInit.main方法,经过socket管道,预加载资源后,进入runSelectLoop方法。
4.ZygoteInit.main
[->ZygoteInit.java]
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
Runnable caller;
try {
// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restart
if (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
// TODO (chriswailes): Wrap these three calls in a helper function?
final String blastulaSocketName =
socketName.equals(ZygoteProcess.ZYGOTE_SOCKET_NAME)
? ZygoteProcess.BLASTULA_POOL_SOCKET_NAME
: ZygoteProcess.BLASTULA_POOL_SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME;
//为zygote注册socket
zygoteServer.createZygoteSocket(socketName);
Zygote.createBlastulaSocket(blastulaSocketName);
Zygote.getSocketFDs(socketName.equals(ZygoteProcess.ZYGOTE_SOCKET_NAME));
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
//预加载资源
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false, 0);
Zygote.nativeSecurityInit();
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
if (startSystemServer) {
//启动systemserver进程
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
// If the return value is null then this is the zygote process
// returning to the normal control flow. If it returns a Runnable
// object then this is a blastula that has finished specializing.
// 初始化胚胎池
caller = Zygote.initBlastulaPool();
if (caller == null) {
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// 当接收到创建进程的请求时唤醒并执行相应工作
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}5.ZS.runSelectLoop
[->ZygoteServer.java]
/**
* Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
* they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
* worth at a time.
*/
Runnable runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> socketFDs = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
//mZygoteSocket是socket通信中的服务端即zygote进程,保存在fds[0]中
socketFDs.add(mZygoteSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
int[] blastulaPipeFDs = Zygote.getBlastulaPipeFDs();
// Space for all of the socket FDs, the Blastula Pool Event FD, and
// all of the open blastula read pipe FDs.
//pollFDs包括socket、Blastula Pool Event 和open blastula read pipe FDs
StructPollfd[] pollFDs =
new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size() + 1 + blastulaPipeFDs.length];
int pollIndex = 0;
for (FileDescriptor socketFD : socketFDs) {
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = socketFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
final int blastulaPoolEventFDIndex = pollIndex;
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = Zygote.sBlastulaPoolEventFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
for (int blastulaPipeFD : blastulaPipeFDs) {
FileDescriptor managedFd = new FileDescriptor();
managedFd.setInt$(blastulaPipeFD);
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = managedFd;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
try {
//处理轮询状态,当pollFDs有事件到来则往下执行,否则阻塞在这里
Os.poll(pollFDs, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
while (--pollIndex >= 0) {
//采用I/O多路复用机制,当接收到客户端发出的连接请求时或者数据处理请求到来
//则往下执行,否则continue,本次循环结束
if ((pollFDs[pollIndex].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (pollIndex == 0) {
// Zygote server socket
//代表mZygoteSocket即fds[0]
//有客户连接请求,创建ZygoteConnection对象并添加到socketFDs
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
socketFDs.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
} else if (pollIndex < blastulaPoolEventFDIndex) {
// Session socket accepted from the Zygote server socket
// 从zygote server中的socket
try {
ZygoteConnection connection = peers.get(pollIndex);
final Runnable command = connection.processOneCommand(this);
if (mIsForkChild) {
// We're in the child. We should always have a command to run at this
// stage if processOneCommand hasn't called "exec".
if (command == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("command == null");
}
return command;
} else {
// We're in the server - we should never have any commands to run.
if (command != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("command != null");
}
// We don't know whether the remote side of the socket was closed or
// not until we attempt to read from it from processOneCommand. This
// shows up as a regular POLLIN event in our regular processing loop.
if (connection.isClosedByPeer()) {
connection.closeSocket();
peers.remove(pollIndex);
socketFDs.remove(pollIndex);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mIsForkChild) {
// We're in the server so any exception here is one that has taken place
// pre-fork while processing commands or reading / writing from the
// control socket. Make a loud noise about any such exceptions so that
// we know exactly what failed and why.
Slog.e(TAG, "Exception executing zygote command: ", e);
// Make sure the socket is closed so that the other end knows
// immediately that something has gone wrong and doesn't time out
// waiting for a response.
ZygoteConnection conn = peers.remove(pollIndex);
conn.closeSocket();
socketFDs.remove(pollIndex);
} else {
// We're in the child so any exception caught here has happened post
// fork and before we execute ActivityThread.main (or any other main()
// method). Log the details of the exception and bring down the process.
Log.e(TAG, "Caught post-fork exception in child process.", e);
throw e;
}
} finally {
// Reset the child flag, in the event that the child process is a child-
// zygote. The flag will not be consulted this loop pass after the Runnable
// is returned.
mIsForkChild = false;
}
} else {
// Either the blastula pool event FD or a blastula reporting pipe.
// blastula pool event FD或者blastula reporting pipe
// If this is the event FD the payload will be the number of blastulas removed.
// If this is a reporting pipe FD the payload will be the PID of the blastula
// that was just specialized.
long messagePayload = -1;
try {
/**
* Number of bytes sent to the Zygote over blastula pipes or the pool event FD
* public static final int BLASTULA_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES = 8;
*/
byte[] buffer = new byte[Zygote.BLASTULA_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES];
int readBytes = Os.read(pollFDs[pollIndex].fd, buffer, 0, buffer.length);
if (readBytes == Zygote.BLASTULA_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES) {
DataInputStream inputStream =
new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer));
messagePayload = inputStream.readLong();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Incomplete read from blastula management FD of size "
+ readBytes);
continue;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (pollIndex == blastulaPoolEventFDIndex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from blastula pool event FD: "
+ ex.getMessage());
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from blastula reporting pipe: "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
continue;
}
if (pollIndex > blastulaPoolEventFDIndex) {
Zygote.removeBlastulaTableEntry((int) messagePayload);
}
int[] sessionSocketRawFDs =
socketFDs.subList(1, socketFDs.size())
.stream()
.mapToInt(fd -> fd.getInt$())
.toArray();
final Runnable command = Zygote.fillBlastulaPool(sessionSocketRawFDs);
if (command != null) {
return command;
}
}
}
}
}第三小节zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult发送请求来建立连接,根据不同的请求做相应的处理:
pollIndex小于blastulaPoolEventFDIndex为来自Zygote server socket的请求;
执行acceptCommandPeer,创建ZygoteConnection对象,并添加socketFDs数值,建立连接后,可以和客户端进行通信,进入processOneCommand方法接受客户端数据,并执行进程创建工作。
pollIndex大于等于blastulaPoolEventFDIndex为胚胎池事件FD或者胚胎上报管道;
读取管道信息,调用fillBlastulaPool方法,创建胚胎(blastula)进程。
5.1 ZC.acceptCommandPeer
/**
* Waits for and accepts a single command connection. Throws
* RuntimeException on failure.
*/
private ZygoteConnection acceptCommandPeer(String abiList) {
try {
return createNewConnection(mZygoteSocket.accept(), abiList);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"IOException during accept()", ex);
}
}
protected ZygoteConnection createNewConnection(LocalSocket socket, String abiList)
throws IOException {
return new ZygoteConnection(socket, abiList);
}客户端发送过来的connect操作,服务端zygote执行accept操作,然后客户端写数据,zygote服务端读数据。
在没有连接的情况下会进入休眠状态,当有新创建的进程发送连接请求时,唤醒zygote进程,创建socket通道,然后执行processOneCommand方法。
6. ZC.processOneCommand
[->ZygoteConnection.java]
/**
* Reads one start command from the command socket. If successful, a child is forked and a
* {@code Runnable} that calls the childs main method (or equivalent) is returned in the child
* process. {@code null} is always returned in the parent process (the zygote).
*
* If the client closes the socket, an {@code EOF} condition is set, which callers can test
* for by calling {@code ZygoteConnection.isClosedByPeer}.
*/
Runnable processOneCommand(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
String args[];
ZygoteArguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
//读取客户端发送过来参数列表
args = Zygote.readArgumentList(mSocketReader);
// TODO (chriswailes): Remove this and add an assert.
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("IOException on command socket", ex);
}
// readArgumentList returns null only when it has reached EOF with no available
// data to read. This will only happen when the remote socket has disconnected.
if (args == null) {
isEof = true;
return null;
}
int pid = -1;
FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
//将客户端传递过来的参数,解析成ZygoteArguments对象格式
parsedArgs = new ZygoteArguments(args);
//进行一序列参数判断
if (parsedArgs.mAbiListQuery) {
handleAbiListQuery();
return null;
}
if (parsedArgs.mPidQuery) {
handlePidQuery();
return null;
}
if (parsedArgs.mPreloadDefault) {
handlePreload();
return null;
}
if (parsedArgs.mPreloadPackage != null) {
handlePreloadPackage(parsedArgs.mPreloadPackage, parsedArgs.mPreloadPackageLibs,
parsedArgs.mPreloadPackageLibFileName, parsedArgs.mPreloadPackageCacheKey);
return null;
}
if (parsedArgs.mApiBlacklistExemptions != null) {
handleApiBlacklistExemptions(parsedArgs.mApiBlacklistExemptions);
return null;
}
if (parsedArgs.mHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate != -1) {
handleHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate(parsedArgs.mHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate);
return null;
}
if (parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities != 0 || parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities != 0) {
throw new ZygoteSecurityException("Client may not specify capabilities: "
+ "permitted=0x" + Long.toHexString(parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities)
+ ", effective=0x" + Long.toHexString(parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities));
}
Zygote.applyUidSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
Zygote.applyInvokeWithSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
Zygote.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
Zygote.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
int[][] rlimits = null;
if (parsedArgs.mRLimits != null) {
rlimits = parsedArgs.mRLimits.toArray(Zygote.INT_ARRAY_2D);
}
int[] fdsToIgnore = null;
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
try {
FileDescriptor[] pipeFds = Os.pipe2(O_CLOEXEC);
childPipeFd = pipeFds[1];
serverPipeFd = pipeFds[0];
Os.fcntlInt(childPipeFd, F_SETFD, 0);
fdsToIgnore = new int[]{childPipeFd.getInt$(), serverPipeFd.getInt$()};
} catch (ErrnoException errnoEx) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to set up pipe for invoke-with", errnoEx);
}
}
/**
* In order to avoid leaking descriptors to the Zygote child,
* the native code must close the two Zygote socket descriptors
* in the child process before it switches from Zygote-root to
* the UID and privileges of the application being launched.
*
* In order to avoid "bad file descriptor" errors when the
* two LocalSocket objects are closed, the Posix file
* descriptors are released via a dup2() call which closes
* the socket and substitutes an open descriptor to /dev/null.
*/
int [] fdsToClose = { -1, -1 };
FileDescriptor fd = mSocket.getFileDescriptor();
if (fd != null) {
fdsToClose[0] = fd.getInt$();
}
fd = zygoteServer.getZygoteSocketFileDescriptor();
if (fd != null) {
fdsToClose[1] = fd.getInt$();
}
fd = null;
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid, parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mMountExternal, parsedArgs.mSeInfo,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote,
parsedArgs.mInstructionSet, parsedArgs.mAppDataDir, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion);
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
//子进程执行
zygoteServer.setForkChild();
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
//见第四大节
return handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd,
parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote);
} else {
// 父进程执行
// In the parent. A pid < 0 indicates a failure and will be handled in
// handleParentProc.
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd);
return null;
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}这里主要是处理客户端返回过来的参数,并调用forkAndSpecialize方法创建进程,返回pid
7.Zygote.forkAndSpecialize
[->Zygote.java]
/**
* @return 0 if this is the child, pid of the child
* if this is the parent, or -1 on error.
*/
public static int forkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int[] fdsToClose,
int[] fdsToIgnore, boolean startChildZygote, String instructionSet, String appDataDir,
int targetSdkVersion) {
//见小节8
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
// Resets nice priority for zygote process.
resetNicePriority();
//见小节9
int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, mountExternal, seInfo, niceName, fdsToClose,
fdsToIgnore, startChildZygote, instructionSet, appDataDir);
// Enable tracing as soon as possible for the child process.
if (pid == 0) {
Zygote.disableExecuteOnly(targetSdkVersion);
Trace.setTracingEnabled(true, runtimeFlags);
// Note that this event ends at the end of handleChildProc,
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "PostFork");
}
//见小节12
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}

Zygote进程有4个子线程分别为ReferenceQueueD、FinalizerDaemon、FinalizerWatchd、HeapTaskDaemon,图中的线程名显示并不完整,是由于底层的进程结构体task_struct是由长度16的char型数组保存。
8. ZygoteHooks.preFork
[->ZygoteHooks.java]
public void preFork() {
Daemons.stop(); //停止4个Daemons子进程
waitUntilAllThreadsStopped(); //等待所有子线程结束
token = nativePreFork(); //完成gc堆得初始化
}8.1 Daemons.stop
[->Daemons.java]
public static void stop() {
HeapTaskDaemon.INSTANCE.stop(); //Java堆整理线程
ReferenceQueueDaemon.INSTANCE.stop(); //引用队列线程
FinalizerDaemon.INSTANCE.stop(); //析构线程
FinalizerWatchdogDaemon.INSTANCE.stop();//析构监控线程
}此守护线程stop方式是先调用目标线程的interrupt方法,然后再调用目标线程join方法,等待线程执行完成。
/**
* Waits for the runtime thread to stop. This interrupts the thread
* currently running the runnable and then waits for it to exit.
*/
public void stop() {
Thread threadToStop;
synchronized (this) {
threadToStop = thread;
thread = null;
}
if (threadToStop == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("not running");
}
interrupt(threadToStop);
while (true) {
try {
threadToStop.join();
return;
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (OutOfMemoryError ignored) {
// An OOME may be thrown if allocating the InterruptedException failed.
}
}
}8.2 waitUntilAllThreadsStopped
[->ZygoteHooks.java]
private static void waitUntilAllThreadsStopped() {
File tasks = new File("/proc/self/task");
// All Java daemons are stopped already. We're just waiting for their OS counterparts to
// finish as well. This shouldn't take much time so spinning is ok here.
// 当/proc中线程数大于1,就让出线程数大于1,才退出循环
while (tasks.list().length > 1) {
Thread.yield();
}
}8.3 nativePreFork
[->dalvik_system_ZygoteHooks.cc]
nativePreFork通过JNI最终调用如下方法:
static jlong ZygoteHooks_nativePreFork(JNIEnv* env, jclass) {
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
CHECK(runtime->IsZygote()) << "runtime instance not started with -Xzygote";
runtime->PreZygoteFork();
if (Trace::GetMethodTracingMode() != TracingMode::kTracingInactive) {
// Tracing active, pause it.
Trace::Pause();
}
// Grab thread before fork potentially makes Thread::pthread_key_self_ unusable.
//将线程转换为long类型并保存到token,该过程是非安全的
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(ThreadForEnv(env));
}
void Runtime::PreZygoteFork() {
//堆的初始化,具体到art虚拟机
heap_->PreZygoteFork();
}
ZygoteHooks.preFork主要功能是停止Zygote的4个Daemon子线程的运行,等待并确保Zygote是单线程(用于fork效率),并等待这些线程的停止,初始化gc堆得工作,并将线程转换为long型并保存到token。
9. nativeForkAndSpecialize
[->com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp]
nativeForkAndSpecialize通过JNC调用如下方法
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize(
JNIEnv* env, jclass, jint uid, jint gid, jintArray gids,
jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits,
jint mount_external, jstring se_info, jstring nice_name,
jintArray managed_fds_to_close, jintArray managed_fds_to_ignore, jboolean is_child_zygote,
jstring instruction_set, jstring app_data_dir) {
jlong capabilities = CalculateCapabilities(env, uid, gid, gids, is_child_zygote);
if (UNLIKELY(managed_fds_to_close == nullptr)) {
ZygoteFailure(env, "zygote", nice_name, "Zygote received a null fds_to_close vector.");
}
std::vector<int> fds_to_close =
ExtractJIntArray(env, "zygote", nice_name, managed_fds_to_close).value();
std::vector<int> fds_to_ignore =
ExtractJIntArray(env, "zygote", nice_name, managed_fds_to_ignore)
.value_or(std::vector<int>());
std::vector<int> blastula_pipes = MakeBlastulaPipeReadFDVector();
fds_to_close.insert(fds_to_close.end(), blastula_pipes.begin(), blastula_pipes.end());
fds_to_ignore.insert(fds_to_ignore.end(), blastula_pipes.begin(), blastula_pipes.end());
fds_to_close.push_back(gBlastulaPoolSocketFD);
if (gBlastulaPoolEventFD != -1) {
fds_to_close.push_back(gBlastulaPoolEventFD);
fds_to_ignore.push_back(gBlastulaPoolEventFD);
}
//见10小节
pid_t pid = ForkCommon(env, false, fds_to_close, fds_to_ignore);
if (pid == 0) {
//见11小节
SpecializeCommon(env, uid, gid, gids, runtime_flags, rlimits,
capabilities, capabilities,
mount_external, se_info, nice_name, false,
is_child_zygote == JNI_TRUE, instruction_set, app_data_dir);
}
return pid;
}
10. ForkCommon
[->com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp]
// Utility routine to fork a process from the zygote.
static pid_t ForkCommon(JNIEnv* env, bool is_system_server,
const std::vector<int>& fds_to_close,
const std::vector<int>& fds_to_ignore) {
//设置子进程的signal信号处理函数
SetSignalHandlers();
// Curry a failure function.
auto fail_fn = std::bind(ZygoteFailure, env, is_system_server ? "system_server" : "zygote",
nullptr, _1);
// Temporarily block SIGCHLD during forks. The SIGCHLD handler might
// log, which would result in the logging FDs we close being reopened.
// This would cause failures because the FDs are not whitelisted.
//
// Note that the zygote process is single threaded at this point.
BlockSignal(SIGCHLD, fail_fn);
// Close any logging related FDs before we start evaluating the list of
// file descriptors.
__android_log_close();
stats_log_close();
// If this is the first fork for this zygote, create the open FD table. If
// it isn't, we just need to check whether the list of open files has changed
// (and it shouldn't in the normal case).
if (gOpenFdTable == nullptr) {
gOpenFdTable = FileDescriptorTable::Create(fds_to_ignore, fail_fn);
} else {
gOpenFdTable->Restat(fds_to_ignore, fail_fn);
}
android_fdsan_error_level fdsan_error_level = android_fdsan_get_error_level();
//fork子进程
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
// The child process.
PreApplicationInit();
// Clean up any descriptors which must be closed immediately
DetachDescriptors(env, fds_to_close, fail_fn);
// Re-open all remaining open file descriptors so that they aren't shared
// with the zygote across a fork.
gOpenFdTable->ReopenOrDetach(fail_fn);
// Turn fdsan back on.
android_fdsan_set_error_level(fdsan_error_level);
} else {
ALOGD("Forked child process %d", pid);
}
// We blocked SIGCHLD prior to a fork, we unblock it here.
UnblockSignal(SIGCHLD, fail_fn);
return pid;
}fork采用copy on write技术,这是linux创建进程的标准方法,调用一次,返回两次,返回值有3中类型。
父进程中,fork返回新创建的子进程pid
子进程中,fork返回0
当出现错误(进程数超过上限或者系统内存不足)时,fork返回负数。
fork主要工作是寻找空闲的进程号pid,然后从父进程中拷贝进程信息,例如代码段和数据段,fork后子进程要执行的代码。Zygote进程是所有Android进程的母体,包括systemserver和各个app进程。zygote利用fork方法生成新的进程,对于新进程A复用Zygote进程本身的资源,再加上新进程A相关的资源,构成新的应用进程A.
copy on write过程:当父子进程任何一方修改内存数据时(on-write时机),才发生缺页中断,从而分配新的物理内存(copy操作)。原理:写时拷贝是指子进程与父进程的页表都指向同一物理内存,fork过程只拷贝父进程的页表,并标记这些页表是可读的。父子进程共用同一份物理内存,如果父子进程任一方想要修改这块物理内存,那么就会触发缺页异常,linux收到改中断便会创建新的物理内存,并将这个两个物理内存都设置为可写状态,从而父子进程各自用用独立的物理内存。
10.1 fork
[->bionic/fork.cpp]
int fork() {
__bionic_atfork_run_prepare();
pthread_internal_t* self = __get_thread();
//fork过程,syscall调用
int result = clone(nullptr,
nullptr,
(CLONE_CHILD_SETTID | CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID | SIGCHLD),
nullptr,
nullptr,
nullptr,
&(self->tid));
if (result == 0) {
// Update the cached pid, since clone() will not set it directly (as
// self->tid is updated by the kernel).
self->set_cached_pid(gettid());
__bionic_atfork_run_child();
} else {
__bionic_atfork_run_parent();
}
return result;
}
在执行clone前后都有相应的回调方法
__bionic_atfork_run_prepare() : fork完成执行子进程回调方法
__bionic_atfork_run_child() : fork完成执行子进程回调方法
__bionic_atfork_run_parent() : fork完成执行父进程回调方法
这个三个方法bionic/pthread_atfork.cpp中,如果有业务需求,可以拓展回调方法
11. SpecializeCommon
[->com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp]
// Utility routine to specialize a zygote child process.
static void SpecializeCommon(JNIEnv* env, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids,
jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits,
jlong permitted_capabilities, jlong effective_capabilities,
jint mount_external, jstring managed_se_info,
jstring managed_nice_name, bool is_system_server,
bool is_child_zygote, jstring managed_instruction_set,
jstring managed_app_data_dir) {
const char* process_name = is_system_server ? "system_server" : "zygote";
auto fail_fn = std::bind(ZygoteFailure, env, process_name, managed_nice_name, _1);
auto extract_fn = std::bind(ExtractJString, env, process_name, managed_nice_name, _1);
auto se_info = extract_fn(managed_se_info);
auto nice_name = extract_fn(managed_nice_name);
auto instruction_set = extract_fn(managed_instruction_set);
auto app_data_dir = extract_fn(managed_app_data_dir);
// Keep capabilities across UID change, unless we're staying root.
if (uid != 0) {
EnableKeepCapabilities(fail_fn);
}
SetInheritable(permitted_capabilities, fail_fn);
DropCapabilitiesBoundingSet(fail_fn);
bool use_native_bridge = !is_system_server &&
instruction_set.has_value() &&
android::NativeBridgeAvailable() &&
android::NeedsNativeBridge(instruction_set.value().c_str());
if (use_native_bridge && !app_data_dir.has_value()) {
// The app_data_dir variable should never be empty if we need to use a
// native bridge. In general, app_data_dir will never be empty for normal
// applications. It can only happen in special cases (for isolated
// processes which are not associated with any app). These are launched by
// the framework and should not be emulated anyway.
use_native_bridge = false;
ALOGW("Native bridge will not be used because managed_app_data_dir == nullptr.");
}
MountEmulatedStorage(uid, mount_external, use_native_bridge, fail_fn);
// If this zygote isn't root, it won't be able to create a process group,
// since the directory is owned by root.
//对于非systemserver子进程并且uid==0,则创建进程组
if (!is_system_server && getuid() == 0) {
const int rc = createProcessGroup(uid, getpid());
if (rc != 0) {
if (rc == -EROFS) {
ALOGW("createProcessGroup failed, kernel missing CONFIG_CGROUP_CPUACCT?");
} else {
ALOGE("createProcessGroup(%d, %d) failed: %s", uid, 0/*pid*/, strerror(-rc));
}
}
}
SetGids(env, gids, fail_fn); //设置group
SetRLimits(env, rlimits, fail_fn); //设置资源limit
if (use_native_bridge) {
// Due to the logic behind use_native_bridge we know that both app_data_dir
// and instruction_set contain values.
android::PreInitializeNativeBridge(app_data_dir.value().c_str(),
instruction_set.value().c_str());
}
if (setresgid(gid, gid, gid) == -1) {
fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("setresgid(%d) failed: %s", gid, strerror(errno)));
}
// Must be called when the new process still has CAP_SYS_ADMIN, in this case,
// before changing uid from 0, which clears capabilities. The other
// alternative is to call prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1) afterward, but that
// breaks SELinux domain transition (see b/71859146). As the result,
// privileged syscalls used below still need to be accessible in app process.
SetUpSeccompFilter(uid);
if (setresuid(uid, uid, uid) == -1) {
fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("setresuid(%d) failed: %s", uid, strerror(errno)));
}
// The "dumpable" flag of a process, which controls core dump generation, is
// overwritten by the value in /proc/sys/fs/suid_dumpable when the effective
// user or group ID changes. See proc(5) for possible values. In most cases,
// the value is 0, so core dumps are disabled for zygote children. However,
// when running in a Chrome OS container, the value is already set to 2,
// which allows the external crash reporter to collect all core dumps. Since
// only system crashes are interested, core dump is disabled for app
// processes. This also ensures compliance with CTS.
int dumpable = prctl(PR_GET_DUMPABLE);
if (dumpable == -1) {
ALOGE("prctl(PR_GET_DUMPABLE) failed: %s", strerror(errno));
RuntimeAbort(env, __LINE__, "prctl(PR_GET_DUMPABLE) failed");
}
if (dumpable == 2 && uid >= AID_APP) {
if (prctl(PR_SET_DUMPABLE, 0, 0, 0, 0) == -1) {
ALOGE("prctl(PR_SET_DUMPABLE, 0) failed: %s", strerror(errno));
RuntimeAbort(env, __LINE__, "prctl(PR_SET_DUMPABLE, 0) failed");
}
}
// Set process properties to enable debugging if required.
if ((runtime_flags & RuntimeFlags::DEBUG_ENABLE_JDWP) != 0) {
EnableDebugger();
}
if (NeedsNoRandomizeWorkaround()) {
// Work around ARM kernel ASLR lossage (http://b/5817320).
int old_personality = personality(0xffffffff);
int new_personality = personality(old_personality | ADDR_NO_RANDOMIZE);
if (new_personality == -1) {
ALOGW("personality(%d) failed: %s", new_personality, strerror(errno));
}
}
SetCapabilities(permitted_capabilities, effective_capabilities, permitted_capabilities, fail_fn);
//设置调度策略
SetSchedulerPolicy(fail_fn);
const char* se_info_ptr = se_info.has_value() ? se_info.value().c_str() : nullptr;
const char* nice_name_ptr = nice_name.has_value() ? nice_name.value().c_str() : nullptr;
if (selinux_android_setcontext(uid, is_system_server, se_info_ptr, nice_name_ptr) == -1) {
fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("selinux_android_setcontext(%d, %d, /"%s/", /"%s/") failed",
uid, is_system_server, se_info_ptr, nice_name_ptr));
}
// Make it easier to debug audit logs by setting the main thread's name to the
// nice name rather than "app_process".
if (nice_name.has_value()) {
SetThreadName(nice_name.value());
} else if (is_system_server) {
SetThreadName("system_server");
}
// Unset the SIGCHLD handler, but keep ignoring SIGHUP (rationale in SetSignalHandlers).
//在子进程中,设置信号SIGHUP的处理器恢复默认行为
UnsetChldSignalHandler();
if (is_system_server) {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(gZygoteClass, gCallPostForkSystemServerHooks);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
fail_fn("Error calling post fork system server hooks.");
}
// Prefetch the classloader for the system server. This is done early to
// allow a tie-down of the proper system server selinux domain.
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(gZygoteInitClass, gCreateSystemServerClassLoader);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
// Be robust here. The Java code will attempt to create the classloader
// at a later point (but may not have rights to use AoT artifacts).
env->ExceptionClear();
}
// TODO(oth): Remove hardcoded label here (b/117874058).
static const char* kSystemServerLabel = "u:r:system_server:s0";
//selinux上下文
if (selinux_android_setcon(kSystemServerLabel) != 0) {
fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("selinux_android_setcon(%s)", kSystemServerLabel));
}
}
//JNI,调用java方法,调用zygote.callPostForkChildHooks[见11.1]
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(gZygoteClass, gCallPostForkChildHooks, runtime_flags,
is_system_server, is_child_zygote, managed_instruction_set);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
fail_fn("Error calling post fork hooks.");
}
}11.1 callPostForkChildHooks
[->Zygote.java]
private static void callPostForkChildHooks(int runtimeFlags, boolean isSystemServer,
boolean isZygote, String instructionSet) {
ZygoteHooks.postForkChild(runtimeFlags, isSystemServer, isZygote, instructionSet);
}
11.2 postForkChild
[->ZygoteHooks.java]
public void postForkChild(int runtimeFlags, boolean isSystemServer, boolean isZygote,
String instructionSet) {
nativePostForkChild(token, runtimeFlags, isSystemServer, isZygote, instructionSet);
Math.setRandomSeedInternal(System.currentTimeMillis());
}11.3 nativePostForkChild
[->dalvik_system_ZygoteHooks.cc]
static void ZygoteHooks_nativePostForkChild(JNIEnv* env,
jclass,
jlong token,
jint runtime_flags,
jboolean is_system_server,
jboolean is_zygote,
jstring instruction_set) {
DCHECK(!(is_system_server && is_zygote));
//此token由8.3创建,记录着当前线程
Thread* thread = reinterpret_cast<Thread*>(token);
// Our system thread ID, etc, has changed so reset Thread state.
// 设置新进程的主线程id
thread->InitAfterFork();
runtime_flags = EnableDebugFeatures(runtime_flags);
hiddenapi::EnforcementPolicy api_enforcement_policy = hiddenapi::EnforcementPolicy::kNoChecks;
bool dedupe_hidden_api_warnings = true;
if ((runtime_flags & DISABLE_VERIFIER) != 0) {
Runtime::Current()->DisableVerifier();
runtime_flags &= ~DISABLE_VERIFIER;
}
if ((runtime_flags & ONLY_USE_SYSTEM_OAT_FILES) != 0) {
Runtime::Current()->GetOatFileManager().SetOnlyUseSystemOatFiles();
runtime_flags &= ~ONLY_USE_SYSTEM_OAT_FILES;
}
api_enforcement_policy = hiddenapi::EnforcementPolicyFromInt(
(runtime_flags & HIDDEN_API_ENFORCEMENT_POLICY_MASK) >> API_ENFORCEMENT_POLICY_SHIFT);
runtime_flags &= ~HIDDEN_API_ENFORCEMENT_POLICY_MASK;
bool profile_system_server = (runtime_flags & PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER) == PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
runtime_flags &= ~PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
if (runtime_flags != 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << StringPrintf("Unknown bits set in runtime_flags: %#x", runtime_flags);
}
// Update tracing.
if (Trace::GetMethodTracingMode() != TracingMode::kTracingInactive) {
Trace::TraceOutputMode output_mode = Trace::GetOutputMode();
Trace::TraceMode trace_mode = Trace::GetMode();
size_t buffer_size = Trace::GetBufferSize();
// Just drop it.
Trace::Abort();
// Only restart if it was streaming mode.
// TODO: Expose buffer size, so we can also do file mode.
if (output_mode == Trace::TraceOutputMode::kStreaming) {
static constexpr size_t kMaxProcessNameLength = 100;
char name_buf[kMaxProcessNameLength] = {};
int rc = pthread_getname_np(pthread_self(), name_buf, kMaxProcessNameLength);
std::string proc_name;
if (rc == 0) {
// On success use the pthread name.
proc_name = name_buf;
}
if (proc_name.empty() || proc_name == "zygote" || proc_name == "zygote64") {
// Either no process name, or the name hasn't been changed, yet. Just use pid.
pid_t pid = getpid();
proc_name = StringPrintf("%u", static_cast<uint32_t>(pid));
}
std::string trace_file = StringPrintf("/data/misc/trace/%s.trace.bin", proc_name.c_str());
Trace::Start(trace_file.c_str(),
-1,
buffer_size,
0, // TODO: Expose flags.
output_mode,
trace_mode,
0); // TODO: Expose interval.
if (thread->IsExceptionPending()) {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
thread->ClearException();
}
}
}
bool do_hidden_api_checks = api_enforcement_policy != hiddenapi::EnforcementPolicy::kNoChecks;
DCHECK(!(is_system_server && do_hidden_api_checks))
<< "SystemServer should be forked with EnforcementPolicy::kDisable";
DCHECK(!(is_zygote && do_hidden_api_checks))
<< "Child zygote processes should be forked with EnforcementPolicy::kDisable";
Runtime::Current()->SetHiddenApiEnforcementPolicy(api_enforcement_policy);
Runtime::Current()->SetDedupeHiddenApiWarnings(dedupe_hidden_api_warnings);
if (api_enforcement_policy != hiddenapi::EnforcementPolicy::kNoChecks &&
Runtime::Current()->GetHiddenApiEventLogSampleRate() != 0) {
// Hidden API checks are enabled, and we are sampling access for the event log. Initialize the
// random seed, to ensure the sampling is actually random. We do this post-fork, as doing it
// pre-fork would result in the same sequence for every forked process.
std::srand(static_cast<uint32_t>(NanoTime()));
}
// Clear the hidden API warning flag, in case it was set.
Runtime::Current()->SetPendingHiddenApiWarning(false);
if (is_zygote) {
// If creating a child-zygote, do not call into the runtime's post-fork logic.
// Doing so would spin up threads for Binder and JDWP. Instead, the Java side
// of the child process will call a static main in a class specified by the parent.
return;
}
if (instruction_set != nullptr && !is_system_server) {
ScopedUtfChars isa_string(env, instruction_set);
InstructionSet isa = GetInstructionSetFromString(isa_string.c_str());
Runtime::NativeBridgeAction action = Runtime::NativeBridgeAction::kUnload;
if (isa != InstructionSet::kNone && isa != kRuntimeISA) {
action = Runtime::NativeBridgeAction::kInitialize;
}
Runtime::Current()->InitNonZygoteOrPostFork(
env, is_system_server, action, isa_string.c_str());
} else {
Runtime::Current()->InitNonZygoteOrPostFork(
env,
is_system_server,
Runtime::NativeBridgeAction::kUnload,
/*isa*/ nullptr,
profile_system_server);
}
}11.4 InitNonZygoteOrPostFork
[->runtime.cc]
void Runtime::InitNonZygoteOrPostFork(
JNIEnv* env,
bool is_system_server,
NativeBridgeAction action,
const char* isa,
bool profile_system_server) {
is_zygote_ = false;
if (is_native_bridge_loaded_) {
switch (action) {
case NativeBridgeAction::kUnload:
//卸载用于跨平台的桥连库
UnloadNativeBridge();
is_native_bridge_loaded_ = false;
break;
case NativeBridgeAction::kInitialize:
//初始化用于跨平台的桥连库
InitializeNativeBridge(env, isa);
break;
}
}
// Create the thread pools.
//创建java堆处理的线程池
heap_->CreateThreadPool();
// Reset the gc performance data at zygote fork so that the GCs
// before fork aren't attributed to an app.
//重置gc性能数据,以保证进程在创建之前的GCs不会计算到当前app上
heap_->ResetGcPerformanceInfo();
// We may want to collect profiling samples for system server, but we never want to JIT there.
if (is_system_server) {
jit_options_->SetUseJitCompilation(false);
jit_options_->SetSaveProfilingInfo(profile_system_server);
if (profile_system_server) {
jit_options_->SetWaitForJitNotificationsToSaveProfile(false);
VLOG(profiler) << "Enabling system server profiles";
}
}
if (!safe_mode_ &&
(jit_options_->UseJitCompilation() || jit_options_->GetSaveProfilingInfo()) &&
jit_ == nullptr) {
// Note that when running ART standalone (not zygote, nor zygote fork),
// the jit may have already been created.
//当flag1被设置,并且还没有创建JIT时,则创建JIT
CreateJit();
}
//设置信号处理函数
StartSignalCatcher();
// Start the JDWP thread. If the command-line debugger flags specified "suspend=y",
// this will pause the runtime (in the internal debugger implementation), so we probably want
// this to come last.
// 启动JDWP线程,当命令debuger的flags指定suspend=y时,则暂停runtime
ScopedObjectAccess soa(Thread::Current());
GetRuntimeCallbacks()->StartDebugger();
}12. postForkCommon
[->ZygoteHooks.java]
public void postForkCommon() {
Daemons.startPostZygoteFork();
}
public static void startPostZygoteFork() {
ReferenceQueueDaemon.INSTANCE.startPostZygoteFork();
FinalizerDaemon.INSTANCE.startPostZygoteFork();
FinalizerWatchdogDaemon.INSTANCE.startPostZygoteFork();
HeapTaskDaemon.INSTANCE.startPostZygoteFork();
}ZygoteHooks的postForkCommon主要功能是fork新进程后,启动zygote的四个Daemon线程,引用队列线程,析构线程,析构监控线程、java堆整理线程。
13. 小结
1.ZygoteInit.main方法,经过socket管道,预加载资源后,进入runSelectLoop方法。
2.runSelectLoop执行acceptCommandPeer,创建ZygoteConnection对象,并添加socketFDs数值,建立连接后,可以和客户端进行通信,进入processOneCommand方法接受客户端数据,并调用forkAndSpecialize方法创建进程。
3.forkAndSpecialize主要功能是
preFork:停止Zygote的4个Daemon线程的运行,初始化gc堆;
nativeForkAndSpecialize:调用fork创建新进程,设置新进程的主线程id,重置gc性能数据,设置信号处理函数等功能、启动JDWP线程。
postForkCommon:启动4个Daemon线程。
到此App进程完成创建的所有工作,执行forkAndSpecialize后,新创建的App进程进入了handleChildProc,后面就是App进程的工作了。
四、新进程运行
在第6小节中processOneCommand过程中调用forkAndSpecialize创建完新进程后,返回值pid=0即运行在子进程,继续开始执行handleChildProc方法。
14. ZC.handleChildProc
[->ZygoteConnection.java]
private Runnable handleChildProc(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs, FileDescriptor[] descriptors,
FileDescriptor pipeFd, boolean isZygote) {
/**
* By the time we get here, the native code has closed the two actual Zygote
* socket connections, and substituted /dev/null in their place. The LocalSocket
* objects still need to be closed properly.
*/
//关闭zygote的socket的连接
closeSocket();
if (descriptors != null) {
try {
Os.dup2(descriptors[0], STDIN_FILENO);
Os.dup2(descriptors[1], STDOUT_FILENO);
Os.dup2(descriptors[2], STDERR_FILENO);
for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd);
}
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reopening stdio", ex);
}
}
if (parsedArgs.mNiceName != null) {
//设置进程名
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.mNiceName);
}
// End of the postFork event.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
//用于检测进程内存泄露或者溢出时设计
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),
pipeFd, parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs);
// Should not get here.
throw new IllegalStateException("WrapperInit.execApplication unexpectedly returned");
} else {
//不是zygote进程
if (!isZygote) {
//执行目标类main方法,见流程15
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
} else {
return ZygoteInit.childZygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
}
}
}15. ZygoteInit.zygoteInit
[->ZygoteInit.java]
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
//重定向log
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
//初始化,见流程15.1
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
//zygote初始化,见流程15.2
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
//应用初始化
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
15.1 commonInit
[-> RuntimeInit.java]
protected static final void commonInit() {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Entered RuntimeInit!");
/*
* set handlers; these apply to all threads in the VM. Apps can replace
* the default handler, but not the pre handler.
*/
//设置默认的异常处理方法
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler();
RuntimeHooks.setUncaughtExceptionPreHandler(loggingHandler);
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new KillApplicationHandler(loggingHandler));
/*
* Install a time zone supplier that uses the Android persistent time zone system property.
*/
//设置时区
RuntimeHooks.setTimeZoneIdSupplier(() -> SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone"));
/*
* Sets handler for java.util.logging to use Android log facilities.
* The odd "new instance-and-then-throw-away" is a mirror of how
* the "java.util.logging.config.class" system property works. We
* can't use the system property here since the logger has almost
* certainly already been initialized.
*/
//重置log配置
LogManager.getLogManager().reset();
new AndroidConfig();
/*
* Sets the default HTTP User-Agent used by HttpURLConnection.
*/
//设置默认的HTTP User-Agent ,用于HttpURLConnection
String userAgent = getDefaultUserAgent();
System.setProperty("http.agent", userAgent);
/*
* Wire socket tagging to traffic stats.
*/
//设置socket的tag,用于流量统计
NetworkManagementSocketTagger.install();
/*
* If we're running in an emulator launched with "-trace", put the
* VM into emulator trace profiling mode so that the user can hit
* F9/F10 at any time to capture traces. This has performance
* consequences, so it's not something you want to do always.
*/
//配置trace
String trace = SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.android.tracing");
if (trace.equals("1")) {
Slog.i(TAG, "NOTE: emulator trace profiling enabled");
Debug.enableEmulatorTraceOutput();
}
initialized = true;
}15.2 nativeZygoteInit
[->AndroidRuntime.cpp]
static void com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
//在AndroidRuntime.cpp中定义
gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit();
}[->app_main.cpp]
virtual void onZygoteInit()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool./n");
proc->startThreadPool(); //启动新的binder线程
}ProcessState::self()主要工作是调用open打开dev/binder驱动设备,再利用mmap映射内核的地址空间,将Binder驱动的fd赋值给ProcessState对象中的mDriverFD,用于交互操作。
startThreadPool用于创建一个binder线程池,不断进行talkWithDriver。
15.3 applicationInit
[-> RuntimeInit.java]
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
//true代表应用程序退出时不调用AppRuntime.onExit,否则会在退出前退出
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
//设置虚拟机的内存利用率的参数为0.75
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
//调用starClass的static方法,见流程16
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
16. findStaticMain
[-> RuntimeInit.java]
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
//通过抛出异常,回到zygoteInit.main方法,这样能清空栈帧,提高栈帧利用率,见流程17
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}MethodAndArgsCaller方法中的m是指main方法,argv是指ActivityThread,根据流程4可知,下一步进入到 caller.run()方法,也即MethodAndArgsCaller.run。
17. MethodAndArgsCaller
[-> RuntimeInit.java]
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
//反射调用ActivityThread.main静态方法,见流程18
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}最后进入ActivityThread.main方法
18. AT.main
[->ActivityThread]
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
//创建主线程looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Find the value for {@link #PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT} if provided on the command line.
// It will be in the format "seq=114"
long startSeq = 0;
if (args != null) {
for (int i = args.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (args[i] != null && args[i].startsWith(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT)) {
startSeq = Long.parseLong(
args[i].substring(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT.length()));
}
}
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
//主线程进入循环状态
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}五、总结
Process.start方法是阻塞操作,直到进程创建完成并返回相应的进程pid时,才完成该方法。
app第一次启动时,其启动所在的进程会通过binder发送消息给Systemserver进程。systemserver进程是从Process.start开始,执行创建进程的操作。
Systemserver进程:通过Process.start方法发起创建新进程请求,会先收集各种新进程uid,gid,nice-name等相关参数,然后通过socket通道发送给zygote进程。
Zygote进程:接收到systemserver进程发送过来的参数后封装成Arguments对象,forAnddSpecialize方法是进程创建过程中最关键的一个过程,具体主要执行下面3个方法。
preFork:停止Zygote的4个Daemon线程(java堆内存整理线程,引用队列线程、析构线程以及监控线程)的运行,初始化gc堆;
nativeForkAndSpecialize:调用fork创建新进程,设置新进程的主线程id,创建java堆处理的线程池,重置gc性能数据,设置信号处理函数等功能、启动JDWP线程。
postForkCommon:启动之前被停止4个Daemon线程。
新进程:进入handleChildProc方法,设置进程名,打开binder驱动,启动新的binder线程,然后设置虚拟机参数,再通过调用目标类的main方法,即ActivityThread.main.
新进程由于会调用nativeZygoteInit,这个过程会调用startThreadPool创建binder线程池,所以每个进程一定至少包含一个Binder线程。
附录
源码路径
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteServer.java
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/ZygoteHooks.java
art/runtime/native/dalvik_system_ZygoteHooks.cc
art/runtime/native/runtime.cc
frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
bionic/libc/bionic/fork.cpp
art/runtime/signal_catcher.cc
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java