在插件化中,hook Activity作为最基本的技术,用来在宿主app中新增Activity,而通常情况下,Activity必须在Manifest中注册在才可以使用,下面将就Android10.0来分析hook Activity的详细过程。
要hook Activity之前,必须知道Activity的启动过程,才能够选择合适的点进行hook,在前面的文章中有分析Android10StartActivity启动过程分析,hook主要是两个点:一是在Activity给AMS之前替换代理的Activity,二是在handler中发送启动Activity时替换为插件的Activity。
分析完了Activity的hook点之后,还有一个重要的问题,如何加载插件的类和资源,只有加载了插件中的类和资源,后面的hook才有意义。
一、类加载
在Android中,将代码编译后会生成apk文件,apk文件里面有一个或多个classes.dex文件,它是所有class文件进行合并,优化后生成。在apk运行时ART虚拟机或Dalvik虚拟机会加载dex文件,加载都是通过ClassLoader实现。
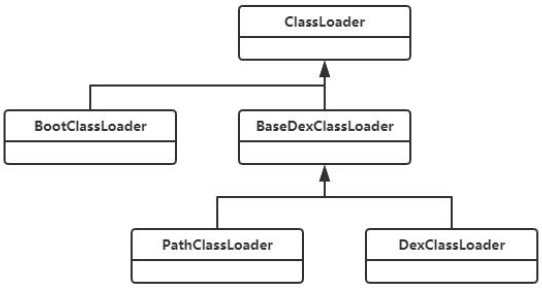
ClassLoader是一个抽象类,实现分为系统类加载器和自定义类加载器。
系统类加载器有三种:
BootClassLoader:用于加载Android Framework中class文件。
PathClassLoader:用于Android应用程序类加载器,可以加载指定的dex,以及jar、zip、apk中的dex。
DexClassLoader:用于加载指定的dex,以及jar、zip、apk中的dex。
1.1 PathClassLoader
[->libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\PathClassLoader.java]
public class PathClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
/**
* Creates a {@code PathClassLoader} that operates on a given list of files
* and directories. This method is equivalent to calling
* {@link #PathClassLoader(String, String, ClassLoader)} with a
* {@code null} value for the second argument (see description there).
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, null, parent);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PathClassLoader} that operates on two given
* lists of files and directories. The entries of the first list
* should be one of the following:
*
*
* JAR/ZIP/APK files, possibly containing a "classes.dex" file as
* well as arbitrary resources.
* Raw ".dex" files (not inside a zip file).
*
*
* The entries of the second list should be directories containing
* native library files.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param librarySearchPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, librarySearchPath, parent);
}
}BaseDexClassLoader
[->libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\BaseDexClassLoader.java]
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
/**
* Hook for customizing how dex files loads are reported.
*
* This enables the framework to monitor the use of dex files. The
* goal is to simplify the mechanism for optimizing foreign dex files and
* enable further optimizations of secondary dex files.
*
* The reporting happens only when new instances of BaseDexClassLoader
* are constructed and will be active only after this field is set with
* {@link BaseDexClassLoader#setReporter}.
*/
/* @NonNull */ private static volatile Reporter reporter = null;
private final DexPathList pathList;
.....
} 1.2 DexClassLoader
[->libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\DexClassLoader.java]
public class DexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
/**
* Creates a {@code DexClassLoader} that finds interpreted and native
* code. Interpreted classes are found in a set of DEX files contained
* in Jar or APK files.
*
* The path lists are separated using the character specified by the
* {@code path.separator} system property, which defaults to {@code :}.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory this parameter is deprecated and has no effect since API level 26.
* @param librarySearchPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, librarySearchPath, parent);
}
}PathClassLoader和DexClassLoader两者都是继承于BaseDexClassLoader,并且类中只有构成方法,实现全部在BaseDexClassLoader中。从源码中可以看出DexClassLoader多个一个optimizedDirectory参数,但是实际上没什么用处,这两者最后调用的super方法一模一样。
1.3 加载原理
类加载器通过loadClass方法加载apk文件中的类。
1.3.1 ClassLoader.loadClass
[->libcore\ojluni\src\main\java\java\lang\ClassLoader.java]
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
// 检查这个类是否已经被加载
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
if (parent != null) {
//如果parent不为空,则调用parent的loadClass进行加载
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
//正常情况下不会走到这里
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
//如果还是找不到,就调用findClass去查找
c = findClass(name);
}
}
return c;
}
private Class<?> findBootstrapClassOrNull(String name){
return null;
}
protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) {
ClassLoader loader;
if (this == BootClassLoader.getInstance())
loader = null;
else
loader = this;
//通过native方法实现查找
return VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass(loader, name);
} 上面类加载的过程就是双亲委派机制。先检查类是否已经被加载,如果已经加载,直接获取并返回。如果没有被加载,parent不为空,则调用parent的loadClass进行加载,依次递归,直到找到或者加载了就返回;如果还没有找到也加载不了,则自己去加载。
BootClassLoader是最后一个加载器,BootClassLoader重写了findClass和loadClass方法,并且在loadClass方法中不再获取parent,从而结束递归。
在所有parent都不能加载的情况下,DexClassLoader加载过程如下,它的父类继承了BaseDexClassLoader,并重写了findClass方法。
1.3.2 BaseDexClassLoader.findClass
[->libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\BaseDexClassLoader.java]
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
//在pathlist中查找指定的class
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
ClassNotFoundException cnfe = new ClassNotFoundException(
"Didn't find class \"" + name + "\" on path: " + pathList);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
cnfe.addSuppressed(t);
}
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
private final DexPathList pathList;
/**
* @hide
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent, boolean isTrusted) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, librarySearchPath, null, isTrusted);
if (reporter != null) {
reportClassLoaderChain();
}
} 1.3.3 DexPathList.findClass
[->\libcore\dalvik\src\main\java\dalvik\system\DexPathList.java]
/**
* List of dex/resource (class path) elements.
* Should be called pathElements, but the Facebook app uses reflection
* to modify 'dexElements' (http://b/7726934).
*/
private Element[] dexElements;
public Class<?> findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
//通过element获取class对象
Class<?> clazz = element.findClass(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
} dexElements初始化在构造函数中完成
DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, File optimizedDirectory, boolean isTrusted) {
...
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions, definingContext, isTrusted);
...
} 生成Element数组,每一个dex对应一个Element
private static Element[] makeDexElements(List<File> files, File optimizedDirectory,
List<IOException> suppressedExceptions, ClassLoader loader, boolean isTrusted) {
Element[] elements = new Element[files.size()];
int elementsPos = 0;
/*
* Open all files and load the (direct or contained) dex files up front.
*/
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
// We support directories for looking up resources. Looking up resources in
// directories is useful for running libcore tests.
elements[elementsPos++] = new Element(file);
} else if (file.isFile()) {
String name = file.getName();
DexFile dex = null;
if (name.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {
// Raw dex file (not inside a zip/jar).
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory, loader, elements);
if (dex != null) {
elements[elementsPos++] = new Element(dex, null);
}
} catch (IOException suppressed) {
System.logE("Unable to load dex file: " + file, suppressed);
suppressedExceptions.add(suppressed);
}
} else {
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory, loader, elements);
} catch (IOException suppressed) {
/*
* IOException might get thrown "legitimately" by the DexFile constructor if
* the zip file turns out to be resource-only (that is, no classes.dex file
* in it).
* Let dex == null and hang on to the exception to add to the tea-leaves for
* when findClass returns null.
*/
suppressedExceptions.add(suppressed);
}
if (dex == null) {
elements[elementsPos++] = new Element(file);
} else {
elements[elementsPos++] = new Element(dex, file);
}
}
if (dex != null && isTrusted) {
dex.setTrusted();
}
} else {
System.logW("ClassLoader referenced unknown path: " + file);
}
}
if (elementsPos != elements.length) {
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, elementsPos);
}
return elements;
} Class对象从Element中获取,每一个Element对应一个dex文件。通过上面的分析,可以想到插件apk的加载方法,通过DexClassLoader加载器加载插件apk,再通过反射的方法获取到宿主的dexElements,最后将插件dexElements和宿主的dexElements合并并赋值给dexElements,其详细流程如下:
1.创建插件的DexClassLoader类加载器,通过反射获取插件中的dexElements
2.获取宿主的PathClassLoader类加载器,通过反射获取宿主的dexElements
3.合并插件和宿主的dexElements,生成新的Element[]
4.最后通过反射将新的Element[]赋值给宿主的dexElements
//获取BaseDexClassLoader类的class
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader");
//获取BaseDexClassLoader类成员变量pathList
Field pathListField = clazz.getDeclaredField("pathList");
pathListField.setAccessible(true);
//获取宿主PathClassLoader
PathClassLoader pathClassLoader = (PathClassLoader) context.getClassLoader();
//获取宿主pathlist值
Object hostPathList = pathListField.get(pathClassLoader);
//获取宿主的dexElements
Class<?> hostPathListClass = hostPathList.getClass();
Field hostDexElementsField = hostPathListClass.getDeclaredField("dexElements");
hostDexElementsField.setAccessible(true);
Object[] hostDexElements = (Object[]) hostDexElementsField.get(hostPathList);
//获取插件pathlist值
DexClassLoader dexClassLoader = new DexClassLoader(apkPath,context.getCacheDir().getAbsolutePath(),null,pathClassLoader);
Object pluginPathList = pathListField.get(dexClassLoader);
//获取插件的dexElements
Class<?> pluginPathListClass = pluginPathList.getClass();
Field pluginDexElementsField = pluginPathListClass.getDeclaredField("dexElements");
pluginDexElementsField.setAccessible(true);
Object[] pluginDexElements = (Object[]) pluginDexElementsField.get(pluginPathList);
//创建新的Element数组
Object[] newDexElements = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(hostDexElements.getClass().getComponentType(),hostDexElements.length+pluginDexElements.length);
System.arraycopy(hostDexElements,0,newDexElements,0,hostDexElements.length);
System.arraycopy(pluginDexElements,0,newDexElements,hostDexElements.length,pluginDexElements.length);
//将新的Element[]赋值给dexElements
hostDexElementsField.set(hostPathList,newDexElements); 这样就完成了插件apk中类的加载,热修复也用到了这样的类加载的原理,不同的是将插件的Elements放在了最前面。
二、资源加载
要加载插件中的资源,可以通过AssetManager来实现,因为资源的加载实际上是通过AssetManager来加载的。AssetManager可以通过文件名访问那些被编译过的应用程序的资源文件也可以访问没有被编译过的应用程序资源文件。
下面分析下AssetManager如何加载资源的,获取资源是通过getResources方法:
在ActivityThread中attach 方法里面的createAppContext创建Context时会设置Resources。
2.1 CL.createAppContext
[->base\core\java\android\app\ContextImpl.java]
static ContextImpl createAppContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo) {
if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, null, null, null, 0,
null);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
return context;
} 2.2 LoadedApk.getResources
[->base\core\java\android\app\LoadedApk.java]
public Resources getResources() {
if (mResources == null) {
final String[] splitPaths;
try {
splitPaths = getSplitPaths(null);
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
// This should never fail.
throw new AssertionError("null split not found");
}
//获取ResourceManager对象,调用getResources获取mResources
mResources = ResourcesManager.getInstance().getResources(null, mResDir,
splitPaths, mOverlayDirs, mApplicationInfo.sharedLibraryFiles,
Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY, null, getCompatibilityInfo(),
getClassLoader());
}
return mResources;
} 2.3 RM.getResources
[->base\core\java\android\app\ResourcesManager.java]
public @Nullable Resources getResources(@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@Nullable String resDir,
@Nullable String[] splitResDirs,
@Nullable String[] overlayDirs,
@Nullable String[] libDirs,
int displayId,
@Nullable Configuration overrideConfig,
@NonNull CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES, "ResourcesManager#getResources");
final ResourcesKey key = new ResourcesKey(
resDir,
splitResDirs,
overlayDirs,
libDirs,
displayId,
overrideConfig != null ? new Configuration(overrideConfig) : null, // Copy
compatInfo);
classLoader = classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
return getOrCreateResources(activityToken, key, classLoader);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES);
}
} 2.4 RM.getOrCreateResources
[->base\core\java\android\app\ResourcesManager.java]
private @Nullable Resources getOrCreateResources(@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@NonNull ResourcesKey key, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader) {
synchronized (this) {
if (DEBUG) {
Throwable here = new Throwable();
here.fillInStackTrace();
Slog.w(TAG, "!! Get resources for activity=" + activityToken + " key=" + key, here);
}
if (activityToken != null) {
final ActivityResources activityResources =
getOrCreateActivityResourcesStructLocked(activityToken);
// Clean up any dead references so they don't pile up.
ArrayUtils.unstableRemoveIf(activityResources.activityResources,
sEmptyReferencePredicate);
// Rebase the key's override config on top of the Activity's base override.
if (key.hasOverrideConfiguration()
&& !activityResources.overrideConfig.equals(Configuration.EMPTY)) {
final Configuration temp = new Configuration(activityResources.overrideConfig);
temp.updateFrom(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
key.mOverrideConfiguration.setTo(temp);
}
ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
if (resourcesImpl != null) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "- using existing impl=" + resourcesImpl);
}
return getOrCreateResourcesForActivityLocked(activityToken, classLoader,
resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
}
// We will create the ResourcesImpl object outside of holding this lock.
} else {
// Clean up any dead references so they don't pile up.
ArrayUtils.unstableRemoveIf(mResourceReferences, sEmptyReferencePredicate);
// Not tied to an Activity, find a shared Resources that has the right ResourcesImpl
ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
if (resourcesImpl != null) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "- using existing impl=" + resourcesImpl);
}
return getOrCreateResourcesLocked(classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
}
// We will create the ResourcesImpl object outside of holding this lock.
}
// If we're here, we didn't find a suitable ResourcesImpl to use, so create one now.
//创建ResourcesImpl对象
ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = createResourcesImpl(key);
if (resourcesImpl == null) {
return null;
}
// Add this ResourcesImpl to the cache.
mResourceImpls.put(key, new WeakReference<>(resourcesImpl));
final Resources resources;
if (activityToken != null) {
resources = getOrCreateResourcesForActivityLocked(activityToken, classLoader,
resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
} else {
resources = getOrCreateResourcesLocked(classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
}
return resources;
}
} 2.5 RM.createResourcesImpl
[->base\core\java\android\app\ResourcesManager.java]
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl createResourcesImpl(@NonNull ResourcesKey key) {
final DisplayAdjustments daj = new DisplayAdjustments(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
daj.setCompatibilityInfo(key.mCompatInfo);
//创建AssetManager
final AssetManager assets = createAssetManager(key);
if (assets == null) {
return null;
}
final DisplayMetrics dm = getDisplayMetrics(key.mDisplayId, daj);
final Configuration config = generateConfig(key, dm);
//将assets对象传入到ResourcesImpl中
final ResourcesImpl impl = new ResourcesImpl(assets, dm, config, daj);
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "- creating impl=" + impl + " with key: " + key);
}
return impl;
} 2.6 RM.createAssetManager
[->base\core\java\android\app\ResourcesManager.java]
protected @Nullable AssetManager createAssetManager(@NonNull final ResourcesKey key) {
final AssetManager.Builder builder = new AssetManager.Builder();
// resDir can be null if the 'android' package is creating a new Resources object.
// This is fine, since each AssetManager automatically loads the 'android' package
// already.
if (key.mResDir != null) {
try {
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(key.mResDir, false /*sharedLib*/,
false /*overlay*/));
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "failed to add asset path " + key.mResDir);
return null;
}
}
if (key.mSplitResDirs != null) {
for (final String splitResDir : key.mSplitResDirs) {
try {
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(splitResDir, false /*sharedLib*/,
false /*overlay*/));
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "failed to add split asset path " + splitResDir);
return null;
}
}
}
if (key.mOverlayDirs != null) {
for (final String idmapPath : key.mOverlayDirs) {
try {
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(idmapPath, false /*sharedLib*/,
true /*overlay*/));
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "failed to add overlay path " + idmapPath);
// continue.
}
}
}
if (key.mLibDirs != null) {
for (final String libDir : key.mLibDirs) {
if (libDir.endsWith(".apk")) {
// Avoid opening files we know do not have resources,
// like code-only .jar files.
try {
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(libDir, true /*sharedLib*/,
false /*overlay*/));
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Asset path '" + libDir +
"' does not exist or contains no resources.");
// continue.
}
}
}
}
//最后通过build完成创建
return builder.build();
} 2.7 AssetManager.addApkAssets
[->base\core\java\android\content\res\AssetManager.java]
public Builder addApkAssets(ApkAssets apkAssets) {
mUserApkAssets.add(apkAssets);
return this;
}
public AssetManager build() {
// Retrieving the system ApkAssets forces their creation as well.
final ApkAssets[] systemApkAssets = getSystem().getApkAssets();
final int totalApkAssetCount = systemApkAssets.length + mUserApkAssets.size();
final ApkAssets[] apkAssets = new ApkAssets[totalApkAssetCount];
System.arraycopy(systemApkAssets, 0, apkAssets, 0, systemApkAssets.length);
final int userApkAssetCount = mUserApkAssets.size();
for (int i = 0; i < userApkAssetCount; i++) {
apkAssets[i + systemApkAssets.length] = mUserApkAssets.get(i);
}
// Calling this constructor prevents creation of system ApkAssets, which we took care
// of in this Builder.
final AssetManager assetManager = new AssetManager(false /*sentinel*/);
assetManager.mApkAssets = apkAssets;
AssetManager.nativeSetApkAssets(assetManager.mObject, apkAssets,
false /*invalidateCaches*/);
return assetManager;
} 2.8 RM.loadApkAssets
[->base\core\java\android\app\ResourcesManager.java]
private @NonNull ApkAssets loadApkAssets(String path, boolean sharedLib, boolean overlay)
throws IOException {
final ApkKey newKey = new ApkKey(path, sharedLib, overlay);
ApkAssets apkAssets = null;
if (mLoadedApkAssets != null) {
apkAssets = mLoadedApkAssets.get(newKey);
if (apkAssets != null) {
return apkAssets;
}
}
// Optimistically check if this ApkAssets exists somewhere else.
final WeakReference<ApkAssets> apkAssetsRef = mCachedApkAssets.get(newKey);
if (apkAssetsRef != null) {
apkAssets = apkAssetsRef.get();
if (apkAssets != null) {
if (mLoadedApkAssets != null) {
mLoadedApkAssets.put(newKey, apkAssets);
}
return apkAssets;
} else {
// Clean up the reference.
mCachedApkAssets.remove(newKey);
}
}
// We must load this from disk.
if (overlay) {
apkAssets = ApkAssets.loadOverlayFromPath(overlayPathToIdmapPath(path),
false /*system*/);
} else {
apkAssets = ApkAssets.loadFromPath(path, false /*system*/, sharedLib);
}
if (mLoadedApkAssets != null) {
mLoadedApkAssets.put(newKey, apkAssets);
}
mCachedApkAssets.put(newKey, new WeakReference<>(apkAssets));
return apkAssets;
}
按照这样的流程比较难hook,看下之前添加的方法addAssetPath,这个方法已经被废弃,但还可以用,hook这个方法比较简单。
/**
* @deprecated Use {@link #setApkAssets(ApkAssets[], boolean)}
* @hide
*/
@Deprecated
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public int addAssetPath(String path) {
return addAssetPathInternal(path, false /*overlay*/, false /*appAsLib*/);
} 1.创建一个AssetManager对象,并调用addAssetPath方法,将插件apk路径作为参数传入
2.将创建的AssetManager对象作为参数,创建一个新的Resourced对象,并返回给插件使用。
public static Resources loadResource(Context context){
try {
AssetManager assetManager = AssetManager.class.newInstance();
Method addAssetPathMethod = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("addAssetPath",String.class);
//加载插件资源
addAssetPathMethod.invoke(assetManager,apkPath);
Resources resources = context.getResources();
return new Resources(assetManager,resources.getDisplayMetrics(),resources.getConfiguration());
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private Resources resources;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//加载插件类
LoadClassUtil.loadClass(this);
//创建新的resources
resources = LoadClassUtil.loadResource(this);
HookUtil.hookAMS();
HookUtil.hookHandler();
}
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
//resources为空,相当于没有重写,不为空是返回新建的resources对象
return resources==null?super.getResources():resources;
}
然后让插件的Activity重写getResources方法,获取的资源就是新创建的resources对象
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
if(getApplication()!=null&&getApplication()!=null){
return getApplication().getResources();
}
return super.getResources();
} 三、hook Activity
首先在宿主里面创建一个ProxyActivity,并且在Manifest中注册(如果需要对应不同启动模式的Activity,可以全部把每种启动模式下的Activity都注册)。当启动插件Activity时,进入AMS之前,通过Hook将插件Activity替换成ProxyActivity,在进入AMS之后,通过handler发送消息时使用hook将ProxyActivity替换成插件的Activity。
startActivity的流程如下图,可以看到这两个具体的hook点
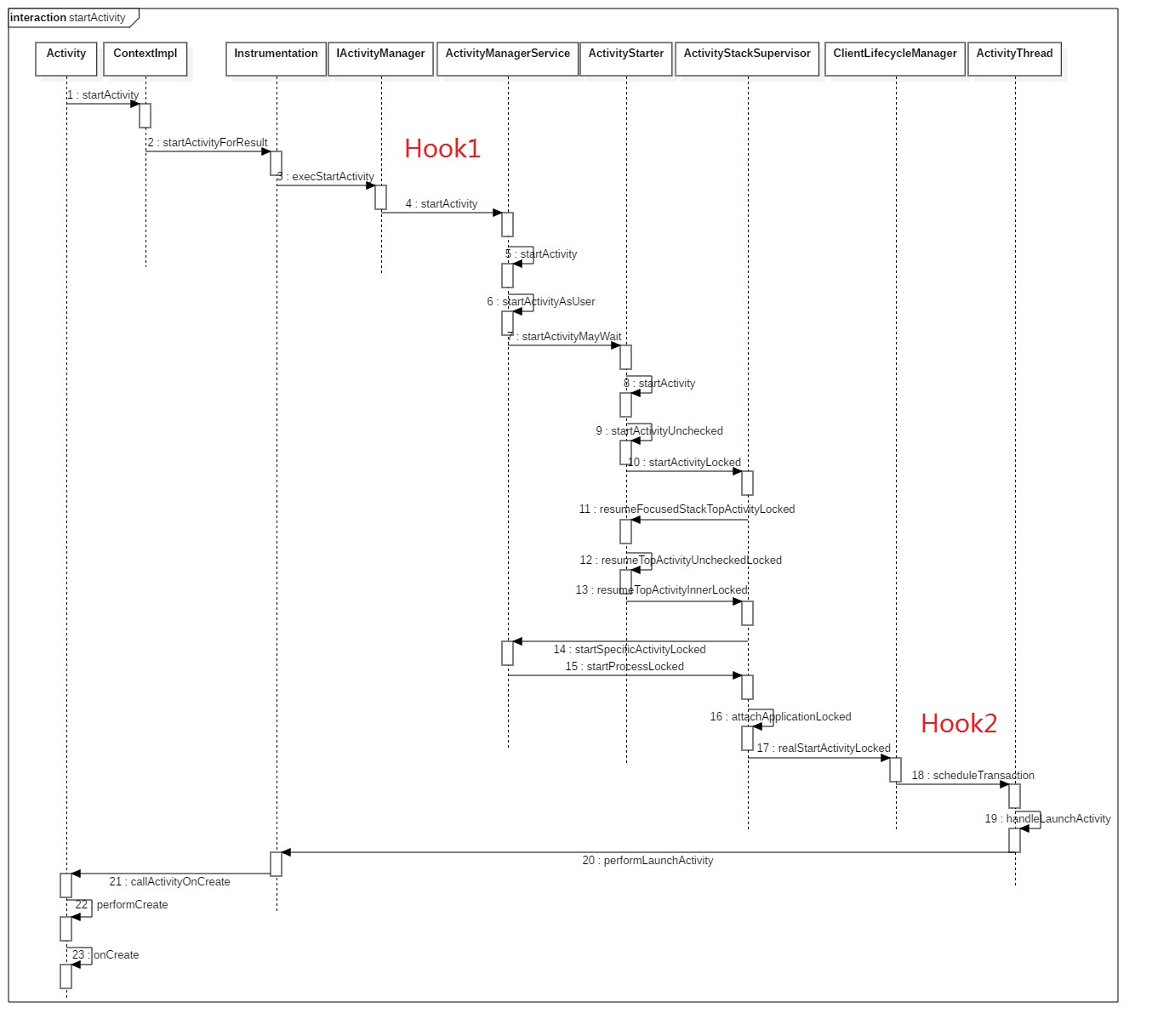
3.1 hook AMS
在进入到AMS之前,这个是最后一步,那么如何将intent换成插件的intent的呢?可以通过动态代理实现。
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, String target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
...
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);
int result = ActivityManager.getService()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target, requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
} ActivityManager.getService具体实现如下
/**
* @hide
*/
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
public abstract class Singleton<T> {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private T mInstance;
protected abstract T create();
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public final T get() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mInstance == null) {
mInstance = create();
}
return mInstance;
}
}
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
//获取AMS的代理
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
}; 第一步获取IActivityManager对象
//获取IActivityManagerSingleton对象,用于获取mIntance
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityManager");
Field singletonFiled = clazz.getDeclaredField("IActivityManagerSingleton");
singletonFiled.setAccessible(true);
Object singleton = singletonFiled.get(null);
//获取Singleton对象
Class<?> singletonClass = Class.forName("android.util.Singleton");
Field mInstanceField = singletonClass.getDeclaredField("mInstance");
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
//获取mInstance对象
final Object mInstance = mInstanceField.get(singleton); 第二步将intent替换成插件的intent
Class<?> iActivityManagerClass = Class.forName("android.app.IActivityManager");
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), new Class[]{iActivityManagerClass},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if("startActivity".equals(method.getName())){
int index = 0;
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
if(args[i] instanceof Intent){
index = i;
break;
}
}
//启动插件的intent
Intent intent = (Intent) args[index];
//启动代理的intent
Intent proxyIntent = new Intent();
proxyIntent.setClassName("com.android.test","com.android.test.ProxyActivity");
//保存插件的intent
proxyIntent.putExtra("target",intent);
args[index] = proxyIntent;
}
return method.invoke(mInstance,args);
}
});
//替换mInstance对象
mInstanceField.set(singleton,proxyInstance); 这样第一个hook点就完成了,下面看下第二步hook点
3.2 hook Handler
在启动Activity之前的操作,Android10.0用状态模式完成Activity的生命周期的启动,那么如何将代理的intent替换成插件的intent的呢?从源码可以看出最后通过scheduleTransaction方法启动Activity,那么是否通过clientTransaction替换intent的呢,通过分析startActivity的启动流程,答案是可以的。
//创建Activity启动事务
// Create activity launch transaction.
final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = ClientTransaction.obtain(app.thread,
r.appToken);
clientTransaction.addCallback(LaunchActivityItem.obtain(new Intent(r.intent),
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
// TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global
// and override configs.
mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(),
mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat,
r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,
r.persistentState, results, newIntents, mService.isNextTransitionForward(),
profilerInfo));
//设置目标事务的状态为onResume
// Set desired final state.
final ActivityLifecycleItem lifecycleItem;
if (andResume) {
lifecycleItem = ResumeActivityItem.obtain(mService.isNextTransitionForward());
} else {
lifecycleItem = PauseActivityItem.obtain();
}
clientTransaction.setLifecycleStateRequest(lifecycleItem);
//通过transaciton方式开始activity生命周期,onCreate,onStart,onResume
// Schedule transaction.
mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction); scheduleTransaction还是要通过Handler发送消息,进入EXECUTE_TRANSACTION分支
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...
case EXECUTE_TRANSACTION:
final ClientTransaction transaction = (ClientTransaction) msg.obj;
mTransactionExecutor.execute(transaction);
if (isSystem()) {
// Client transactions inside system process are recycled on the client side
// instead of ClientLifecycleManager to avoid being cleared before this
// message is handled.
transaction.recycle();
}
// TODO(lifecycler): Recycle locally scheduled transactions.
break;
....
} 那么要替换intent首先需要hook handleMessage
//获取ActivityThread对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Field sCurrentActivityThreadField = clazz.getDeclaredField("sCurrentActivityThread");
sCurrentActivityThreadField.setAccessible(true);
Object activityThread = sCurrentActivityThreadField.get(null);
//获取handler
Field mHField = clazz.getDeclaredField("mH");
mHField.setAccessible(true);
Object mH = mHField.get(activityThread);
//获取callback对象
Field mCallbackField = Handler.class.getDeclaredField("mCallback");
mCallbackField.setAccessible(true);
mCallbackField.set(mH, new Handler.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what){
case 159:
try {
//获取List<ClientTransactionItem> mActivityCallbacks对象
Class<?> clientTransactionClass = msg.obj.getClass();
Field mActivityCallbacksField = clientTransactionClass.getDeclaredField("mActivityCallbacks");
mActivityCallbacksField.setAccessible(true);
List mActivityCallbacks = (List) mActivityCallbacksField.get(msg.obj);
for(int i=0;i<mActivityCallbacks.size();i++){ if(mActivityCallbacks.get(i).getClass().getName().equals("android.app.servertransaction.LaunchActivityItem")){
//获取LaunchActivityItem
Object launchActivityItem = mActivityCallbacks.get(i);
Class<?> launchActivityItemClass = launchActivityItem.getClass();
Field mIntentField = launchActivityItemClass.getDeclaredField("mIntent");
mIntentField.setAccessible(true);
//代理intent
Intent proxyIntent = (Intent) mIntentField.get(launchActivityItem);
//插件intent
Intent intent = proxyIntent.getParcelableExtra("target");
//插件intent替换代理intent
proxyIntent.setComponent(intent.getComponent());
}
} hook了handleMessage后,通过LaunchActivityItem中的mIntent完成代理intent的替换。
四、总结
hook Activity涉及的技术比较多,Activity的启动流程,类加载,动态代理,资源加载,反射,binder机制等,只有在掌握了这些技术的基础上才能够完成插件化技术的开发。
本文介绍了hook Activity的具体实现方法,通过该方法引申出类的加载和资源加载的原理,并分析具体插件的加载实现,后面结合之前文章分析的Android10StartActivity启动过程分析,引出了两个具体的hook点:
1.在ActivityManager.getService().startActivity时通过反射获取IActivityManager对象,startActivity时将插件的Activity替换成代理的Activity;
2.反射获取ActivityThread对象,通过获取类成员变量mH,重新设置callback,将handleMessage中的EXECUTE_TRANSACTION分支进行hook,在mActivityCallbacks中找到LaunchActivityItem,将其类成员变量mIntent替换成插件的Activity,这样就完成的插件Activity的启动过程。