一. 概述
前面文章都是介绍了两个线程InputReader和InputDispatcher的工作过程。在InputDispatcher的过程讲到 调用InputChanel通过socket与远程进程通信,本文便展开讲解这个socket是如何建立的。
对于InputReader和InputDispatcher都是运行在system_server进程; 用户点击的界面往往可能是某一个app,而每个app一般地都运行在自己的进程,这里就涉及到跨进程通信,app进程是如何与system进程建立通信。
要解答这些问题,从Activity最基本的创建过程开始说起。我们都知道一般地Activity对应一个应用窗口, 每一个窗口对应一个ViewRootImpl。窗口是如何添加到Activity的,从Activity.onCreate()为起点讲解。
二. UI线程
众所周知,Activity的生命周期的回调方法都是运行在主线程,也称之为UI线程,所有UI相关的操作都需要运行在该线程。本文虽然是UI线程,但并非只介绍所有运行在UI线程的流程,文中还涉及binder thread。
2.1 onCreate
[-> Activity.java]
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_account_bind);
...
}
Activity启动是由system进程控制:
- handleLaunchActivity():会调用Activity.onCreate(), 该方法内再调用setContentView(),经过AMS与WMS的各种交互,层层调用后,进入step2
- handleResumeActivity():会调用Activity.makeVisible(),该方法继续调用便会执行到WindowManagerImpl.addView(), 该方法内部再调用WindowManagerGlobal.addView(),
2.2 addView
[-> WindowManagerGlobal.java]
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
//[见小节2.3]
ViewRootImpl root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
//[见小节2.3.3]
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
...
}
2.3 ViewRootImpl
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
//获取IWindowSession的代理类【见小节2.3.1】
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
mDisplay = display;
mThread = Thread.currentThread(); //主线程
mWindow = new W(this);
mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();
...
}
2.3.1 getWindowSession
[-> WindowManagerGlobal.java]
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
//获取IMS的代理类
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
//获取WMS的代理类
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
//经过Binder调用,最终调用WMS[见小节2.3.2]
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {...},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
}
return sWindowSession
}
}
2.3.2 WMS.openSession
public IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback, IInputMethodClient client,
IInputContext inputContext) {
//创建Session对象
Session session = new Session(this, callback, client, inputContext);
return session;
}
再次经过Binder将数据写回app进程,则获取的便是Session的代理对象。
2.3.3 setView
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
...
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel(); //创建InputChannel对象
}
//通过Binder调用,进入system进程的Session[见小节2.4]
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
...
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
//创建WindowInputEventReceiver对象[见3.1]
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建Java层的InputChannel对象mInputChannel
- 向WMS注册InputChannel信息,通过InputChannel.openInputChannelPair创建的socket pair,将其中的客户端赋值给mInputChannel.
- 创建WindowInputEventReceiver对象
跨进程调用,进入binder thread执行如下方法:
2.4 Session.addToDisplay
[-> Session.java]
final class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
Rect outOutsets, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
//[见小节2.5]
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outInputChannel);
}
}
2.5 WMS.addToDisplay
[-> WindowManagerService.java]
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
InputChannel outInputChannel) {
...
//创建WindowState【见小节2.5.1】
WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token,
attachedWindow, appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayContent);
if (outInputChannel != null && (attrs.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
//根据WindowState的HashCode以及title来生成InputChannel名称
String name = win.makeInputChannelName();
//创建一对InputChannel[见小节2.6]
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);
//将socket服务端保存到WindowState的mInputChannel
win.setInputChannel(inputChannels[0]);
//socket客户端传递给outInputChannel [见小节2.7]
inputChannels[1].transferTo(outInputChannel);
//利用socket服务端作为参数[见小节2.8]
mInputManager.registerInputChannel(win.mInputChannel, win.mInputWindowHandle);
}
...
boolean focusChanged = false;
if (win.canReceiveKeys()) {
//新添加window能接收按下操作,则更新聚焦窗口。
focusChanged = updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS,
false /*updateInputWindows*/);
}
...
if (focusChanged) {
mInputMonitor.setInputFocusLw(mCurrentFocus, false /*updateInputWindows*/);
}
//设置当前聚焦窗口【见小节2.5.2】
mInputMonitor.updateInputWindowsLw(false /*force*/);
}
inputChannels数组:
- inputChannels[0]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(server); - inputChannels[1]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(client);
其中:
- 服务端inputChannels[0]保存到WindowState的mInputChannel;
- 客户端inputChannels[1]传递给outInputChannel,最终传递给ViewRootImpl的mInputChannel;
2.5.1 WindowState初始化
[-> WindowState.java]
WindowState(WindowManagerService service, Session s, IWindow c, WindowToken token,
WindowState attachedWindow, int appOp, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams a,
int viewVisibility, final DisplayContent displayContent) {
...
WindowState appWin = this;
while (appWin.mAttachedWindow != null) {
appWin = appWin.mAttachedWindow;
}
WindowToken appToken = appWin.mToken;
while (appToken.appWindowToken == null) {
WindowToken parent = mService.mTokenMap.get(appToken.token);
if (parent == null || appToken == parent) {
break;
}
appToken = parent;
}
mAppToken = appToken.appWindowToken;
//创建InputWindowHandle对象
mInputWindowHandle = new InputWindowHandle(
mAppToken != null ? mAppToken.mInputApplicationHandle : null, this,
displayContent.getDisplayId());
}
2.5.2 updateInputWindowsLw
[-> InputMonitor.java]
public void updateInputWindowsLw(boolean force) {
...
final InputWindowHandle dragWindowHandle = mService.mDragState.mDragWindowHandle;
if (dragWindowHandle != null) {
//将dragWindowHandle赋值给mInputWindowHandles
addInputWindowHandleLw(dragWindowHandle);
}
...
//将当前mInputWindowHandles传递到native【】
mService.mInputManager.setInputWindows(mInputWindowHandles);
...
}
setInputWindows的调用链:(最终设置mFocusedWindowHandle值)
-> IMS.setInputWindows
-> NativeInputManager::setInputWindows
-> InputDispatcher::setInputWindows
dragWindowHandle的初始化过程:
View.startDrag
Session.prepareDrag
WMS.prepareDragSurface
mDragState = new DragState(...);
Session.performDrag
DragState.register
mDragWindowHandle = new InputWindowHandle(...);
2.6 openInputChannelPair
[-> InputChannel.java]
public static InputChannel[] openInputChannelPair(String name) {
return nativeOpenInputChannelPair(name);
}
这个过程的主要功能
- 创建两个socket通道(非阻塞, buffer上限32KB)
- 创建两个InputChannel对象;
- 创建两个NativeInputChannel对象;
- 将nativeInputChannel保存到Java层的InputChannel的成员变量mPtr
2.6.1 nativeOpenInputChannelPair
[-> android_view_InputChannel.cpp]
static jobjectArray android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair(JNIEnv* env,
jclass clazz, jstring nameObj) {
const char* nameChars = env->GetStringUTFChars(nameObj, NULL);
String8 name(nameChars);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(nameObj, nameChars);
sp<InputChannel> serverChannel;
sp<InputChannel> clientChannel;
//创建一对socket[见小节2.6.2]
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);
//创建Java数组
jobjectArray channelPair = env->NewObjectArray(2, gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz, NULL);
...
//创建NativeInputChannel对象[见小节2.6.3]
jobject serverChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env,
new NativeInputChannel(serverChannel));
...
//创建NativeInputChannel对象[见小节2.6.3]
jobject clientChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env,
new NativeInputChannel(clientChannel));
...
//将client和server 两个插入到channelPair
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 0, serverChannelObj);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 1, clientChannelObj);
return channelPair;
}
2.6.2 openInputChannelPair
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(const String8& name,
sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) {
int sockets[2];
//真正创建socket对的地方【核心】
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) {
...
return result;
}
int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE; //32k
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
String8 serverChannelName = name;
serverChannelName.append(" (server)");
//创建InputChannel对象
outServerChannel = new InputChannel(serverChannelName, sockets[0]);
String8 clientChannelName = name;
clientChannelName.append(" (client)");
//创建InputChannel对象
outClientChannel = new InputChannel(clientChannelName, sockets[1]);
return OK;
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建socket pair; (
非阻塞式的socket) - 设置两个socket的接收和发送的buffer
上限为32KB; - 创建client和server的Native层InputChannel对象;
- sockets[0]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(server); - sockets[1]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
(client)
- sockets[0]所对应的InputChannel名称的后缀为
创建InputChannel对象位于文件InputTransport.cpp,如下:
InputChannel::InputChannel(const String8& name, int fd) :
mName(name), mFd(fd) {
//将socket设置成非阻塞方式
int result = fcntl(mFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
}
另外,创建NativeInputChannel对象位于文件android_view_InputChannel.cpp,如下:
NativeInputChannel::NativeInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) :
mInputChannel(inputChannel), mDisposeCallback(NULL) {
}
2.6.3 android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel
[-> android_view_InputChannel.cpp]
static jobject android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(JNIEnv* env,
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel) {
//创建Java的InputChannel
jobject inputChannelObj = env->NewObject(gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz,
gInputChannelClassInfo.ctor);
if (inputChannelObj) {
//将nativeInputChannel保存到Java层的InputChannel的成员变量mPtr
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj, nativeInputChannel);
}
return inputChannelObj;
}
static void android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj,
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel) {
env->SetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr,
reinterpret_cast<jlong>(nativeInputChannel));
}
此处:
- gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz是指Java层的InputChannel类
- gInputChannelClassInfo.ctor是指Java层的InputChannel构造方法;
- gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr是指Java层的InputChannel的成员变量mPtr;
2.7 transferTo
[-> InputChannel.java]
public void transferTo(InputChannel outParameter) {
nativeTransferTo(outParameter);
}
2.7.1 nativeTransferTo
[-> android_view_InputChannel.cpp]
static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
jobject otherObj) {
if (android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj) != NULL) {
return; //当Java层的InputChannel.mPtr不为空,则返回
}
//将当前inputChannels[1]的mPtr赋值给nativeInputChannel
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);
// 将该nativeInputChannel保存到outInputChannel的参数
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj, nativeInputChannel);
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);
}
inputChannels[1].transferTo(outInputChannel)主要功能:
- 当outInputChannel.mPtr不为空,则直接返回;否则进入step2;
- 将inputChannels[1].mPtr的值赋给outInputChannel.mPtr;
- 清空inputChannels[1].mPtr值;
也就是将socket客户端inputChannels[1]传递给outInputChannel;
2.8 IMS.registerInputChannel
[-> InputManagerService.java]
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel,
InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle) {
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, false);
}
- inputChannel是指inputChannels[0],即socket服务端;
- inputWindowHandle是指WindowState.mInputWindowHandle;
2.8.1 nativeRegisterInputChannel
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj, jobject inputWindowHandleObj, jboolean monitor) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle =
android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle(env, inputWindowHandleObj);
//[见小节2.8.2]
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(
env, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
...
if (! monitor) {
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
}
}
2.8.2 registerInputChannel
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
status_t NativeInputManager::registerInputChannel(JNIEnv* /* env */,
const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) {
//[见小节2.8.3]
return mInputManager->getDispatcher()->registerInputChannel(
inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
}
mInputManager是指NativeInputManager初始化过程创建的InputManager对象(C++).
2.8.3 registerInputChannel
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
status_t InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
...
//创建Connection[见小节2.8.4]
sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd.add(fd, connection);
...
//将该fd添加到Looper监听[见小节2.8.5]
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
}
mLooper->wake(); //connection改变, 则唤醒looper
return OK;
}
将新创建的connection保存到mConnectionsByFd成员变量,“InputDispatcher”线程的Looper添加对socket服务端的监听功能; 当该socket有消息时便会唤醒该线程工作。
2.8.4 初始化Connection
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
InputDispatcher::Connection::Connection(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) :
status(STATUS_NORMAL), inputChannel(inputChannel), inputWindowHandle(inputWindowHandle),
monitor(monitor),
inputPublisher(inputChannel), inputPublisherBlocked(false) {
}
其中InputPublisher初始化位于文件InputTransport.cpp
InputPublisher:: InputPublisher(const sp<InputChannel>& channel) :
mChannel(channel) {
}
此处inputChannel是指前面openInputChannelPair创建的socket服务端,将其同时保存到Connection.inputChannel和InputPublisher.mChannel。
2.8.5 Looper.addFd
[-> system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp]
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, Looper_callbackFunc callback, void* data) {
// 此处的callback为handleReceiveCallback
return addFd(fd, ident, events, callback ? new SimpleLooperCallback(callback) : NULL, data);
}
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, const sp<LooperCallback>& callback, void* data) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Request request;
request.fd = fd;
request.ident = ident;
request.events = events;
request.seq = mNextRequestSeq++;
request.callback = callback; //是指SimpleLooperCallback
request.data = data;
if (mNextRequestSeq == -1) mNextRequestSeq = 0;
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex < 0) {
//通过epoll监听fd
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.add(fd, request); //该fd的request加入到mRequests队列
} else {
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.replaceValueAt(requestIndex, request);
}
}
return 1;
}
此处Loop便是“InputDispatcher”线程的Looper,将socket服务端的fd采用epoll机制注册监听.
小节
虽然本文介绍的UI线程的工作,
- [小节2.1 ~ 2.3]: 运行在UI线程;
- [小节2.4 ~ 2.8]:通过IWindowSession的Binder IPC调用,运行在system_server的binder thread;
ViewRootImpl的setView()过程:
- 创建socket pair,作为InputChannel:
- socket服务端保存到system_server中的WindowState的mInputChannel;
- socket客户端通过binder传回到远程进程的UI主线程ViewRootImpl的mInputChannel;
- IMS.registerInputChannel()注册InputChannel,监听socket服务端:
- Loop便是“InputDispatcher”线程的Looper;
- 回调方法handleReceiveCallback。
三. WindowInputEventReceiver
接下来,看看【小节2.3.3】创建WindowInputEventReceiver对象
3.1 WindowInputEventReceiver初始化
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
//inputChannel是指socket客户端,Looper是指UI线程的Looper
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper); //【见小节3.2】
}
...
}
3.2 InputEventReceiver
[-> InputEventReceiver.java]
public InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
...
mInputChannel = inputChannel;
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue(); //UI线程消息队列
//【加小节3.3】
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),
inputChannel, mMessageQueue);
}
3.3 nativeInit
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,
jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
//获取UI主线程的消息队列
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
//创建NativeInputEventReceiver对象【见小节3.4】
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,
receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue);
//【见小节3.5】
status_t status = receiver->initialize();
...
receiver->incStrong(gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(receiver.get());
}
3.4 NativeInputEventReceiver
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
class NativeInputEventReceiver : public LooperCallback {
InputConsumer mInputConsumer;
sp<MessageQueue> mMessageQueue;
int mFdEvents;
bool mBatchedInputEventPending;
...
NativeInputEventReceiver::NativeInputEventReceiver(JNIEnv* env,
jobject receiverWeak, const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<MessageQueue>& messageQueue) :
mReceiverWeakGlobal(env->NewGlobalRef(receiverWeak)),
//【见3.4.1】
mInputConsumer(inputChannel), mMessageQueue(messageQueue),
mBatchedInputEventPending(false), mFdEvents(0) {
}
}
3.4.1 InputConsumer
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
InputConsumer::InputConsumer(const sp<InputChannel>& channel) :
mResampleTouch(isTouchResamplingEnabled()),
mChannel(channel), mMsgDeferred(false) {
}
此处inputChannel是指socket客户端。
3.5 initialize
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() {
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT); //【见小节3.6】
return OK;
}
3.6 setFdEvents
[-> android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp]
void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
if (mFdEvents != events) {
mFdEvents = events;
int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();
if (events) {
//将socket客户端的fd添加到主线程的消息池【见小节3.6.1】
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, NULL);
} else {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);
}
}
}
3.6.1 Looper.addFd
[-> system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp]
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events, const sp<LooperCallback>& callback, void* data) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Request request;
request.fd = fd;
request.ident = ident;
request.events = events;
request.seq = mNextRequestSeq++;
request.callback = callback; //是指ativeInputEventReceiver
request.data = data;
if (mNextRequestSeq == -1) mNextRequestSeq = 0;
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex < 0) {
//通过epoll监听fd
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.add(fd, request); //该fd的request加入到mRequests队列
} else {
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, & eventItem);
...
mRequests.replaceValueAt(requestIndex, request);
}
}
return 1;
}
此处的Looper便是UI主线程的Looper,将socket客户端的fd添加到UI线程的Looper来监听,回调方法为NativeInputEventReceiver。
四. 总结
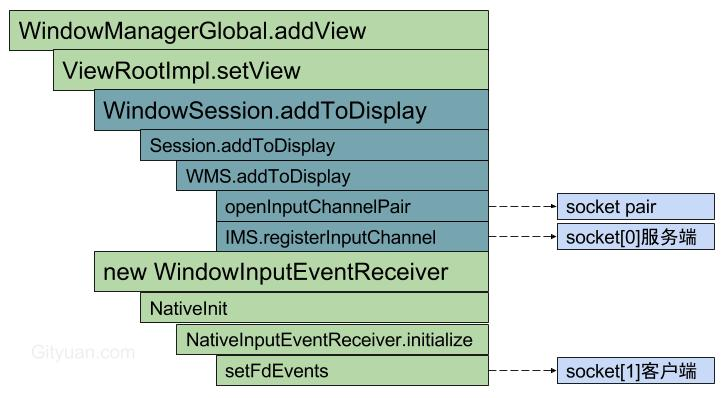
首先,通过openInputChannelPair来创建socket pair,作为InputChannel:
- socket服务端保存到system_server中的WindowState的mInputChannel;
- socket客户端通过binder传回到远程进程的UI主线程ViewRootImpl的mInputChannel;
紧接着,完成了两个线程的epoll监听工作:
- [小节2.8]IMS.registerInputChannel(): “InputDispatcher”线程监听socket服务端,收到消息后回调InputDispatcher.handleReceiveCallback();
- [小节3.6]setFdEvents(): UI主线程监听socket客户端,收到消息后回调NativeInputEventReceiver.handleEvent().
有了这些“InputDispatcher”和“UI”主线程便可以进行跨进程通信与交互。