一、概述
global reference使用不当,就会引发lobal reference overflow异常问题,为了解决这个问题,从Android 9.0开始新增了限制策略。
先来看看虚拟机的一些基本知识。每一个进程都必须有一个JavaVM,且只有一个,是Java虚拟机在JNI层的代表, JNI 全局只有一个;每一个线程都有一个JNIEnv,JNIEnv一个线程相关的结构体, 代表Java 在本线程的运行环境。每个虚拟机Runtime实例由调用Runtime::Create来创建,该过程包含创建JavaVMExt, Heap, Thread, ClassLinker等,调用Runtime::Start完成最后的初始化工作。再来看一张类图了解JavaVM、JNIEnv以及Runtime的核心成员和方法。
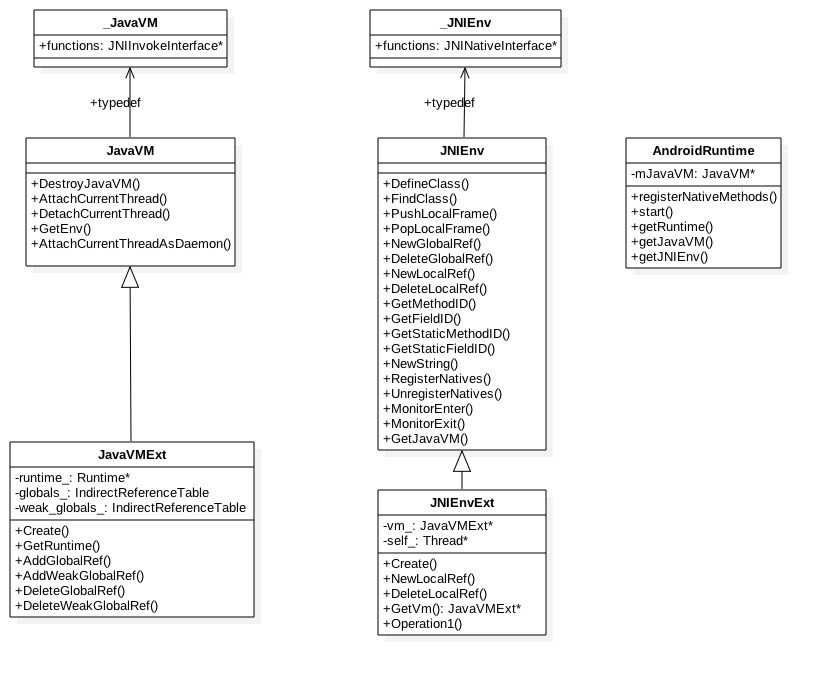
1.1 JavaVM
[-> java_vm_ext.cc]
JavaVMExt::JavaVMExt(Runtime* runtime,
const RuntimeArgumentMap& runtime_options,
std::string* error_msg)
: runtime_(runtime),
force_copy_(runtime_options.Exists(RuntimeArgumentMap::JniOptsForceCopy)),
//见小节【1.3】
globals_(kGlobalsMax, kGlobal, IndirectReferenceTable::ResizableCapacity::kNo, error_msg),
libraries_(new Libraries),
unchecked_functions_(&gJniInvokeInterface),
weak_globals_(kWeakGlobalsMax, kWeakGlobal,
IndirectReferenceTable::ResizableCapacity::kNo, error_msg),
allow_accessing_weak_globals_(true),
weak_globals_add_condition_("weak globals add condition",
(CHECK(Locks::jni_weak_globals_lock_ != nullptr),
*Locks::jni_weak_globals_lock_)),
env_hooks_() {
functions = unchecked_functions_;
SetCheckJniEnabled(runtime_options.Exists(RuntimeArgumentMap::CheckJni));
}
JavaVMExt初始化的过程,从ResizableCapacity::kNo可以看出该容量上限是不允许扩容的,根据kGlobalsMax = 51200,kWeakGlobalsMax = 51200,说明每个进程的全局引用和弱全局引用的上限是51200个,记录在JavaVMExt的IndirectReferenceTable类型成员变量。
关于kGlobal是引用类型,定义如下:
enum IndirectRefKind {
kHandleScopeOrInvalid = 0, // 栈的间接引用表或无效引用
kLocal = 1, // 本地引用
kGlobal = 2, // 全局引用
kWeakGlobal = 3, // 弱全局引用
kLastKind = kWeakGlobal
};
说明:
- 本地引用:只在native方法的一次调用过程有效,方法一旦返回则会被自动释放,可通过NewLocalRef/DeleteLocalRef来主动管理本地引用,比如JNI函数NewObject创建一个实例就是局部引用。
- 全局引用:在释放之前一直有效,不会被垃圾回收,可跨越多线程、多个native方法使用,可通过NewGlobalRef/DeleteGlobalRef来主动管理本地引用。
- 弱全局引用:同样可以跨越多线程、多个native方法使用,但不会阻止垃圾回收。可通过NewGolableWeakRef/DeleteGloablWeakRef管理。
关于globals_构造过程,见下面的[小节1.3]。
1.2 JNIEnv
[-> jni_env_ext.cc]
JNIEnvExt::JNIEnvExt(Thread* self_in, JavaVMExt* vm_in, std::string* error_msg)
: self_(self_in),
vm_(vm_in),
local_ref_cookie_(kIRTFirstSegment),
locals_(kLocalsInitial, kLocal, IndirectReferenceTable::ResizableCapacity::kYes, error_msg),
monitors_("monitors", kMonitorsInitial, kMonitorsMax),
critical_(0),
check_jni_(false),
runtime_deleted_(false) {
MutexLock mu(Thread::Current(), *Locks::jni_function_table_lock_);
check_jni_ = vm_in->IsCheckJniEnabled();
functions = GetFunctionTable(check_jni_);
unchecked_functions_ = GetJniNativeInterface();
}
JNIEnv初始化过程依次将当前的Thread和JavaVMExt对象记录在JNIEnvExt的成员变量self_和vm_。 此处创建IndirectReferenceTable本地引用表的上限为512个引用实体(kLocalsInitial = 512)。
另外说明,在jni.h文件中JNIEnv结构体在C++里面通过typedef关键词定义,其类型为_JNIEnv,该结构体内部有一个JNINativeInterface类型的指针;在C里面则直接通过typedef关键词定义,其类型为JNINativeInterface类型的指针,C/C++下的差异是编译器相关,但其功能是一样的。
#if defined(__cplusplus)
typedef _JNIEnv JNIEnv;
typedef _JavaVM JavaVM;
#else
typedef const struct JNINativeInterface* JNIEnv;
typedef const struct JNIInvokeInterface* JavaVM;
#endif
因此使用过程也就有所不同,如下所示:
//C语言版本
jsize len = (*env)->GetArrayLength(env,array);
//C++语言版本
jsize len =env->GetArrayLength(array);
1.3 IndirectReferenceTable
[-> indirect_reference_table.cc]
IndirectReferenceTable::IndirectReferenceTable(size_t max_count,
IndirectRefKind desired_kind,
ResizableCapacity resizable,
std::string* error_msg)
: segment_state_(kIRTFirstSegment),
kind_(desired_kind),
max_entries_(max_count),
current_num_holes_(0),
resizable_(resizable) {
const size_t table_bytes = max_count * sizeof(IrtEntry);
table_mem_map_.reset(MemMap::MapAnonymous("indirect ref table", nullptr, table_bytes,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, false, false, error_msg));
if (table_mem_map_.get() == nullptr && error_msg->empty()) {
*error_msg = "Unable to map memory for indirect ref table";
}
if (table_mem_map_.get() != nullptr) {
table_ = reinterpret_cast<IrtEntry*>(table_mem_map_->Begin());
} else {
table_ = nullptr;
}
segment_state_ = kIRTFirstSegment;
last_known_previous_state_ = kIRTFirstSegment;
}
再来看看IndirectReferenceTable对象的核心成员变量:
class IndirectReferenceTable {
private:
IRTSegmentState segment_state_;
std::unique_ptr<MemMap> table_mem_map_; // 用于存储引用表的map
IrtEntry* table_; //用于存储IndirectReference实体对象
const IndirectRefKind kind_; //引用类型
size_t max_entries_; //引用个数上限
size_t current_num_holes_; //当前可用的空槽
IRTSegmentState last_known_previous_state_;
ResizableCapacity resizable_;
...
}
IndirectReferenceTable对象中的max_entries_用于记录引用表的引用个数上限:
- JavaVM对象的IndirectReferenceTable引用表的引用个数上限等于51200个,不可扩容
- JNIEnv对象的IndirectReferenceTable引用表的引用个数上限等于512个,可扩容
二、global reference管理
先来看看gloabl reference的添加引用和移除引用的过程。
2.1 添加引用
2.1.1 NewGlobalRef
[-> jni_internal.cc]
static jobject NewGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
ObjPtr<mirror::Object> decoded_obj = soa.Decode<mirror::Object>(obj);
return soa.Vm()->AddGlobalRef(soa.Self(), decoded_obj); //【小节2.1.2】
}
JNIEnv的NewGlobalRef过程主要实现是调用所在的JavaVM的AddGlobalRef来添加全局引用。
2.1.2 AddGlobalRef
[-> java_vm_ext.cc]
jobject JavaVMExt::AddGlobalRef(Thread* self, ObjPtr<mirror::Object> obj) {
if (obj == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
IndirectRef ref;
std::string error_msg;
{
WriterMutexLock mu(self, *Locks::jni_globals_lock_);
//obj加入全局引用表【小节2.1.3】
ref = globals_.Add(kIRTFirstSegment, obj, &error_msg);
}
return reinterpret_cast<jobject>(ref);
}
此处globals_的数据类型为IndirectReferenceTable,是JavaVMExt对象的成员变量。
2.1.3 IndirectReferenceTable.Add
[-> indirect_reference_table.cc]
IndirectRef IndirectReferenceTable::Add(IRTSegmentState previous_state,
ObjPtr<mirror::Object> obj,
std::string* error_msg) {
size_t top_index = segment_state_.top_index;
if (top_index == max_entries_) {
//当引用个数达到上限,且不允许扩容的情况下,则直接返回
if (resizable_ == ResizableCapacity::kNo) {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "JNI ERROR (app bug): " << kind_ << " table overflow "
<< "(max=" << max_entries_ << ")"
<< MutatorLockedDumpable<IndirectReferenceTable>(*this);
*error_msg = oss.str();
return nullptr;
}
...
// 对于允许扩容的情况下,尝试将容量翻倍
std::string inner_error_msg;
if (!Resize(max_entries_ * 2, &inner_error_msg)) {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "JNI ERROR (app bug): " << kind_ << " table overflow "
<< "(max=" << max_entries_ << ")" << std::endl
<< MutatorLockedDumpable<IndirectReferenceTable>(*this)
<< " Resizing failed: " << inner_error_msg;
*error_msg = oss.str();
return nullptr;
}
}
...
IndirectRef result;
size_t index;
//当存在可用的空槽时,从table_顶部往下开始遍历查找,直到找到空槽为止
if (current_num_holes_ > 0) {
IrtEntry* p_scan = &table_[top_index - 1];
--p_scan;
while (!p_scan->GetReference()->IsNull()) {
DCHECK_GE(p_scan, table_ + previous_state.top_index);
--p_scan;
}
index = p_scan - table_; //找到目标空槽
current_num_holes_--; //可用空槽个数减一
} else {
index = top_index++; //若没有空槽,则添加到队尾
segment_state_.top_index = top_index;
}
table_[index].Add(obj);
result = ToIndirectRef(index);
return result;
}
向IndirectReferenceTable表中添加全局引用的过程是不允许扩容的,保证引用个数小于上限,否则记录将JNI ERROR的信息记录在error_msg,并直接返回nullptr。接着需要查找reference所归属的槽位。
- 当存在可用空槽(current_num_holes_>0)时,从table_顶部往下开始遍历查找,直到找到空槽为止,并将可用槽位个数减1;
- 当没有空槽,则将reference添加到队尾
2.2 移除引用
2.2.1 DeleteGlobalRef
[-> jni_internal.cc]
static void DeleteGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
JavaVMExt* vm = down_cast<JNIEnvExt*>(env)->GetVm();
Thread* self = down_cast<JNIEnvExt*>(env)->self_;
vm->DeleteGlobalRef(self, obj); // 【小节2.2.2】
}
JNIEnv的DeleteGlobalRef过程主要实现是调用所在的JavaVM的DeleteGlobalRef来添加全局引用。
2.2.2 DeleteGlobalRef
[-> java_vm_ext.cc]
void JavaVMExt::DeleteGlobalRef(Thread* self, jobject obj) {
if (obj == nullptr) {
return;
}
{
WriterMutexLock mu(self, *Locks::jni_globals_lock_);
//【小节2.2.3】
if (!globals_.Remove(kIRTFirstSegment, obj)) {
LOG(WARNING) << "JNI WARNING: DeleteGlobalRef(" << obj << ") "
<< "failed to find entry";
}
}
CheckGlobalRefAllocationTracking();
}
2.2.3 IndirectReferenceTable.Remove
[-> indirect_reference_table.cc]
bool IndirectReferenceTable::Remove(IRTSegmentState previous_state, IndirectRef iref) {
const uint32_t top_index = segment_state_.top_index;
const uint32_t bottom_index = previous_state.top_index;
...
// 保证index属于有效的范围区间
const uint32_t idx = ExtractIndex(iref);
if (idx < bottom_index) {
return false;
}
if (idx >= top_index) {
return false;
}
RecoverHoles(previous_state);
if (idx == top_index - 1) {
...
//table_表中对应的槽位置空
*table_[idx].GetReference() = GcRoot<mirror::Object>(nullptr);
if (current_num_holes_ != 0) {
uint32_t collapse_top_index = top_index;
while (--collapse_top_index > bottom_index && current_num_holes_ != 0) {
if (!table_[collapse_top_index - 1].GetReference()->IsNull()) {
break;
}
current_num_holes_--; //位于最上方的空槽,则减少当前可用的空槽个数
}
segment_state_.top_index = collapse_top_index; //更新表的顶部编号
} else {
segment_state_.top_index = top_index - 1;
}
} else {
// 不是最上面的条目,则会产生一个空槽。判断当前是否已为空槽,用于防止删除两次,弄乱空槽个数
if (table_[idx].GetReference()->IsNull()) {
return false;
}
*table_[idx].GetReference() = GcRoot<mirror::Object>(nullptr); //置空
current_num_holes_++; //空槽个数+1
}
return true;
}
2.3 小节
有了前面的准备,可知道每个进程的global reference的上限为51200个,如果达到个数上限,则会在下一次添加引用的过程[小节2.1.3]中抛出 Abort message: ‘art/runtime/indirect_reference_table.cc:258] JNI ERROR (app bug): global reference table overflow (max=51200)’。
引用的添加和移除都是成对出现的,常见的使用场景是JNI调用过程中使用JNIEnv的NewGlobalRef()和DeleteGlobalRef()方法,使用过程一定要记得成对出现,否则有可能导致global reference overflow问题。
三、案例
3.1 linkToDeath导致溢出
Abort message: 'art/runtime/indirect_reference_table.cc:258] JNI ERROR (app bug): global reference table overflow (max=51200)'
backtrace:
#00 pc 0000000000079208 /system/lib64/libc.so (tgkill+8)
#01 pc 0000000000076480 /system/lib64/libc.so (pthread_kill+64)
#02 pc 00000000000249a0 /system/lib64/libc.so (raise+24)
#03 pc 000000000001ce8c /system/lib64/libc.so (abort+52)
#04 pc 000000000047eeec /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art7Runtime5AbortEPKc+472)
#05 pc 00000000000e7564 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art10LogMessageD2Ev+1320)
#06 pc 00000000002745cc /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art22IndirectReferenceTable3AddEjPNS_6mirror6ObjectE+324)
#07 pc 0000000000325c6c /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art9JavaVMExt12AddGlobalRefEPNS_6ThreadEPNS_6mirror6ObjectE+68)
#08 pc 0000000000364b04 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art3JNI12NewGlobalRefEP7_JNIEnvP8_jobject+604)
#09 pc 00000000000ffd54 /system/lib64/libandroid_runtime.so
#10 pc 0000000002204a34 /system/framework/arm64/boot-framework.oat (offset 0x1986000) (android.os.BinderProxy.linkToDeath+160)
#11 pc 0000000001512ef4 /system/framework/oat/arm64/services.odex (offset 0xf68000)
linkToDeath(DeathRecipient recipient, int flags)是一个native方法,该过程会调用在JavaDeathRecipient对象初始化过程会NewGlobalRef
3.1.1 JavaDeathRecipient
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
class JavaDeathRecipient : public IBinder::DeathRecipient
{
public:
class JavaDeathRecipient : public IBinder::DeathRecipient
{
public:
JavaDeathRecipient(JNIEnv* env, jobject object, const sp<DeathRecipientList>& list)
: mVM(jnienv_to_javavm(env)), mObject(env->NewGlobalRef(object)),
mObjectWeak(NULL), mList(list)
{
list->add(this); //将当前对象sp添加到列表
android_atomic_inc(&gNumDeathRefs);
incRefsCreated(env); //增加引用计数
}
}
void binderDied(const wp<IBinder>& who)
{
if (mObject != NULL) {
JNIEnv* env = javavm_to_jnienv(mVM);
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(gBinderProxyOffsets.mClass,
gBinderProxyOffsets.mSendDeathNotice, mObject);
sp<DeathRecipientList> list = mList.promote();
if (list != NULL) {
AutoMutex _l(list->lock());
mObjectWeak = env->NewWeakGlobalRef(mObject);
env->DeleteGlobalRef(mObject); //移除全局引用
mObject = NULL;
}
}
}
void clearReference()
{
sp<DeathRecipientList> list = mList.promote();
if (list != NULL) {
list->remove(this);
}
}
protected:
virtual ~JavaDeathRecipient()
{
android_atomic_dec(&gNumDeathRefs);
JNIEnv* env = javavm_to_jnienv(mVM);
if (mObject != NULL) {
env->DeleteGlobalRef(mObject); //移除全局引用
} else {
env->DeleteWeakGlobalRef(mObjectWeak);
}
}
private:
JavaVM* const mVM;
jobject mObject;
jweak mObjectWeak;
wp<DeathRecipientList> mList;
}
说明:
- JavaDeathRecipient对象创建的过程,会执行env->NewGlobalRef()为recipient创建相应的全局引用
- JavaDeathRecipient对象析构和binderDied死亡回调过程,会执行env->DeleteGlobalRef移除全局引用
- clearReference()过程,将DeathRecipientList从list移除,从而能触发对象析构来移除
这里需要重点注意linkToDeath和unlinkToDeath需要配合出现。
3.2 javaObjectForIBinder导致溢出
Abort message: 'art/runtime/indirect_reference_table.cc:258] JNI ERROR (app bug): global reference table overflow (max=51200)'
backtrace:
#00 pc 000000000006ac34 /system/lib64/libc.so (tgkill+8)
#01 pc 00000000000683c4 /system/lib64/libc.so (pthread_kill+68)
#02 pc 0000000000023ae4 /system/lib64/libc.so (raise+28)
#03 pc 000000000001e284 /system/lib64/libc.so (abort+60)
#04 pc 00000000004322b8 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art7Runtime5AbortEv+324)
#05 pc 0000000000136204 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art10LogMessageD2Ev+3136)
#06 pc 0000000000273604 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art22IndirectReferenceTable3AddEjPNS_6mirror6ObjectE+1964)
#07 pc 0000000000309400 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art9JavaVMExt12AddGlobalRefEPNS_6ThreadEPNS_6mirror6ObjectE+56)
#08 pc 000000000033f624 /system/lib64/libart.so (_ZN3art3JNI12NewGlobalRefEP7_JNIEnvP8_jobject+320)
#09 pc 00000000000e6ca8 /system/lib64/libandroid_runtime.so (_ZN7android20javaObjectForIBinderEP7_JNIEnvRKNS_2spINS_7IBinderEEE+412)
#10 pc 00000000000daa1c /system/lib64/libandroid_runtime.so
#11 pc 0000000002c5ec50 /system/framework/arm64/boot.oat (offset 0x28a0000)
从Android 9.0之前的版本中再javaObjectForIBinder()会执行NewGlobalRef,从Android 9.0开始,Google优化了该问题,采用新的实现方案,改动比较多,这里就不再展开,有兴趣的可自行查看。
3.3 解决方案
所有应用进程以及其他一些native进程都会system_server通信,有很多API接口的内部实现涉及到linkToDeath使用,某些应用滥用公开接口引发Global reference数量过多而导致系统重启的问题。从Android 9.0开始,在native层中保存每个uid下所有的Binder Proxy记录,从而可以定位哪个应用滥用并将其杀掉,以保证系统的健壮性和可靠性。对于此类滥用的行为会打印如下日志:
Killing 15015:com.gityuan.appdemo/u0a176 (adj 0): Too many Binders sent to SYSTEM
比如在Android 6.0的原生版本,App中不断调用AppOpsManager的startWatchingMode()就能导致手机重启,小米手机早已修复这个问题。当前从Android 9.0版本开始,Google原生系统刚解决此类问题。
3.3.1 setBinderProxyCountCallback
[-> ActivityManagerService.java]
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, TimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
...
synchronized (this) {
//【小节3.3.2】
BinderInternal.nSetBinderProxyCountWatermarks(6000,5500);
//【小节3.3.3】
BinderInternal.nSetBinderProxyCountEnabled(true);
//【小节3.3.4】
BinderInternal.setBinderProxyCountCallback(
new BinderInternal.BinderProxyLimitListener() {
@Override
public void onLimitReached(int uid) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Uid " + uid + " sent too many Binders to uid "
+ Process.myUid());
if (uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Skipping kill (uid is SYSTEM)");
} else {
//当触发水线,则杀掉发送Binder请求过多的进程
killUid(UserHandle.getAppId(uid), UserHandle.getUserId(uid),
"Too many Binders sent to SYSTEM");
}
}
}, mHandler);
}
...
}
3.3.2 nSetBinderProxyCountWatermarks
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static void android_os_BinderInternal_setBinderProxyCountWatermarks(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz,
jint high, jint low)
{
BpBinder::setBinderProxyCountWatermarks(high, low); //【见下文】
}
[-> BpBinder.cpp]
uint32_t BpBinder::sBinderProxyCountHighWatermark = 2500;
uint32_t BpBinder::sBinderProxyCountLowWatermark = 2000;
void BpBinder::setBinderProxyCountWatermarks(int high, int low) {
AutoMutex _l(sTrackingLock);
sBinderProxyCountHighWatermark = high;
sBinderProxyCountLowWatermark = low;
}
每个进程默认的Binder代理数量的水线区间为[2000,2500],对于system_server进程的水线区间为[5500,6000]。
3.3.3 nSetBinderProxyCountEnabled
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static void android_os_BinderInternal_setBinderProxyCountEnabled(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz,
jboolean enable)
{
BpBinder::setCountByUidEnabled((bool) enable); //【见下文】
}
[-> BpBinder.cpp]
void BpBinder::setCountByUidEnabled(bool enable)
{
sCountByUidEnabled.store(enable);
}
sCountByUidEnabled的数据类型为std::atomic_bool,这是一个原子操作的bool,保证了多线程并发访问的安全问题。
3.3.4 setBinderProxyCountCallback
[-> BinderInternal.java]
public static void setBinderProxyCountCallback(BinderProxyLimitListener listener,
@NonNull Handler handler) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(handler,
"Must provide NonNull Handler to setBinderProxyCountCallback when setting "
+ "BinderProxyLimitListener");
//【见下文】
sBinderProxyLimitListenerDelegate.setListener(listener, handler);
}
注意,此处handler不能为空
[-> BinderInternal.java]
public class BinderInternal {
static final BinderProxyLimitListenerDelegate sBinderProxyLimitListenerDelegate =
new BinderProxyLimitListenerDelegate();
...
public static void binderProxyLimitCallbackFromNative(int uid) {
//执行notifyClient回调方法
sBinderProxyLimitListenerDelegate.notifyClient(uid);
}
static private class BinderProxyLimitListenerDelegate {
private BinderProxyLimitListener mBinderProxyLimitListener;
private Handler mHandler;
void setListener(BinderProxyLimitListener listener, Handler handler) {
synchronized (this) {
mBinderProxyLimitListener = listener;
mHandler = handler;
}
}
void notifyClient(final int uid) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mBinderProxyLimitListener != null) {
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mBinderProxyLimitListener.onLimitReached(uid);
}
});
}
}
}
}
}
setListener设置好Binder代理限制的监听器,以及执行回调的Handler对象。当收到native层传递的某个进程使用system_server的binder代理超过水线,则在mHandler所在线程中执行onLimitReached()方法。
3.3.5 notifyClient
接下来,再来看看native层回调通知的触发时机
在int_register_android_os_BinderInternal()过程调用BpBinder的setLimitCallback方法将android_os_BinderInternal_proxyLimitcallback保存在Bpbinder的sLimitCallback。
binder_proxy_limit_callback BpBinder::sLimitCallback;
BpBinder* BpBinder::create(int32_t handle) {
int32_t trackedUid = -1;
if (sCountByUidEnabled) {
//获取对端的uid
trackedUid = IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingUid();
AutoMutex _l(sTrackingLock);
uint32_t trackedValue = sTrackingMap[trackedUid];
if (CC_UNLIKELY(trackedValue & LIMIT_REACHED_MASK)) {
if (sBinderProxyThrottleCreate) {
return nullptr;
}
} else {
//超过高位的水线
if ((trackedValue & COUNTING_VALUE_MASK) >= sBinderProxyCountHighWatermark) {
ALOGE("Too many binder proxy objects sent to uid %d from uid %d (%d proxies held)",
getuid(), trackedUid, trackedValue);
sTrackingMap[trackedUid] |= LIMIT_REACHED_MASK;
//当binder代理个数超过高水位线,则执行回调方法
if (sLimitCallback) sLimitCallback(trackedUid);
...
}
}
sTrackingMap[trackedUid]++;
}
return new BpBinder(handle, trackedUid);
}
sLimitCallback调用链最终达到AMS中的[3.3.1]的onLimitReached过程,杀掉目标进程并打印日志。
android_os_BinderInternal_proxyLimitcallback
binderProxyLimitCallbackFromNative
notifyClient
onLimitReached
3.5 小节
所有应用进程以及其他一些native进程都会system_server通信,有很多API接口的内部实现涉及到linkToDeath使用,某些应用滥用公开接口引发Global reference数量过多而导致系统重启的问题。从Android 9.0开始,在native层中保存每个uid下所有的Binder Proxy记录,当某个应用向system_server发起的binder代理对象超过6000个,则意味着该应用滥用API,则并将其杀掉,以保证系统的健壮性和可靠性。这一点需要应用要按规范使用接口,比如每次调用startWatchingMode接口后,当不再需要使用时,应该执行相应的配对方法stopWatchingMode,否则会不断增加binder proxy数量只会增加而不减少,当达到阈值就会被系统所杀。
同理,还有类似的方法对:
- linkToDeath():该方法内会调用new JavaDeathRecipient(),在创建recipient对象过程需要调用NewGlobalRef来添加全局引用,防止recipient被回收。
- unlinkToDeath():该方法内会调用clearReference()将当前JavaDeathRecipient对象从列表中移除,从而会执行JavaDeathRecipient的析构函数,调用DeleteGlobalRef来移除全局引用。
还有一点需要说明,对于linkToDeath()后,在收到binderDied()过程本身也会移除全局引用。即便如此,对于建立死亡讣告情况,如果不在需要了,还是建议主动unlinkToDeath()。为了避免全局引用溢出问题,以上两方法需要配对出现,对于发生全局引用溢出问题,需要定位具体是哪个引用导致的,可以从日志中查询”global reference table dump”关键,会打印出最近的TOP 10引用实体,具体问题还需要结合上下文来分析,在最新Android 9.0已修复该问题。